
Australian Journal of Chemistry
Volume 68 Number 5 2015
CH14658Diaryliodonium Salts: Aryl Transfer Reagents for Alkyne Difunctionalization
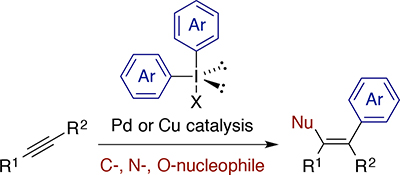
In recent years, hypervalent iodine reagents have emerged as powerful tools in synthesis. This highlight paper describes recent developments in the application of diaryliodonium salts for a variety of transformations. It is shown how the extremely electrophilic nature of these reagents can be exploited to difunctionalize alkynes in cascade reactions to access complex scaffolds.
CH14712Diethylaluminium Azide: A Versatile Reagent in Organic Synthesis
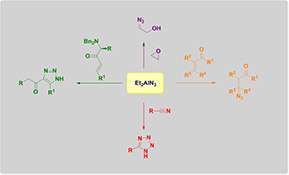
The activated azide donor Et2AlN3 is a powerful reagent not only for epoxide ring-openings or Michael-additions, but also, as reported recently, for high-yielding 1H-tetrazol synthesis.
CH14484Ligand Constraints and Synthesis of Metal–Organic Polyhedra
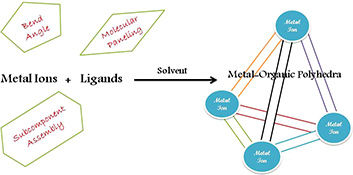
This review highlights the intercession of ligand constraints and the role of various concepts such as molecular panelling and subcomponent self-assembly in the synthesis of metal–organic polyhedra. This includes discrete architectures of various geometries having an internal cavity of appropriate size and nature suitable enough for a range of applications.
CH14380Synthesis and Structure of a Novel Substituted Benzothiazolyl-N-phenyl-2-pyridinecarbothioamide; Kinetics of Formation and Electrochemistry of Two of its Palladium Pincer Complexes
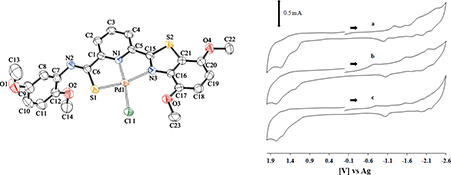
The synthesis of bis-N-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarbothioamide, 6-(4,7-dimethoxy-2-benzothiazolyl)-N-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-pyridinecarbothioamide, and the pincer palladium(ii) chloride, and acetate coordination compounds of the latter species are reported. The electrochemical properties, stability constants for the palladium complex formations, the kinetics of formation and the associated thermodynamic parameters are also presented, and the efficacy of the pincer system in the Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction is explored.
CH14341Structures and Photoluminescence Properties of Four Cadmium(II) Coordination Polymers Synthesized by Rigid Ligands and N-Donor Ligands
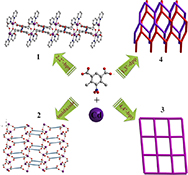
Four metal–organic coordination polymers have been solvothermally synthesized and characterized based on rigid ligands and N-donor ligands.
CH14344ZnII Complexes Based on Hybrid N-Pyrazole, N′-imine Ligands: Synthesis, X-Ray Crystal Structure, NMR Characterisation, and 3D Supramolecular Properties
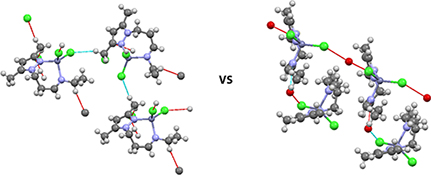
We present new ligands N-[3-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propylidene]ethylamine (L1) and N-[3-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propylidene]propylamine (L2) and their reactivity towards ZnII. Complete characterisation of compounds [ZnCl2(L)] (L = L1 (1) and L2 (2)) by analytical and spectroscopic methods and the resolution of structures by single X-ray diffraction are presented. The three-dimensional supramolecular structure through different intra- and intermolecular contacts is also studied.
CH14347Structural Diversity and Fluorescence Regulation of Three ZnII Coordination Polymers Assembled from Mixed Ligands Tectons
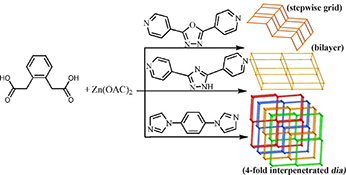
The mixed-ligand strategy involving 1,2-phenylenediacetic acid and various nitrogen-rich co-ligands produce three new Zn coordination polymers, which display a vast diversity of structures from two-dimensional (2D) stepwise grids, 2D double layers to three-dimensional (3D)→3D 4-fold interpenetrating diamondoid networks and various ligand-based fluorescence emissions.
CH14441Solvatomorphism and Electronic Communication in FeIII N,N-Bis(salicylidene)-1,3-propanediamine Dimers
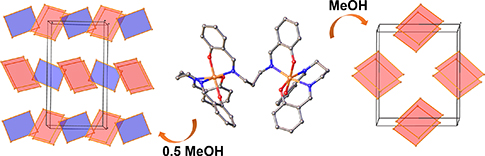
Two solvatomorphs of [(salpn)Fe(μ2-salpn)Fe(salpn)]·nMeOH (H2salpn = N,N′-bis(salicylidene)-1,3-propanediamine, n = 0.5MeOH (1) and MeOH (2)) are prepared. Structural analysis reveals different packing motifs in the structures resulting in an increased number of layers in 1. Electrochemical studies unexpectedly show weak electronic communication between the FeIII centres in these dimers.
CH14293Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of a Series of Ag/ZnO Nanocomposites and Evaluation of Their Photocatalytic Activities under Multi-Mode Photodegradation
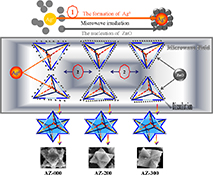
A series of nanocomposites Ag/ZnO were prepared under different microwave power irradiation which combined with sedimentation, of which ZnO precursor particles were assembled as the characteristic of the cubic lattice of metallic silver. The different microwave power irradiation has an effect on the shapes, physical chemistry properties, and photocatalytic activities of Ag/ZnO.
CH14312Investigation of the Rotational Isomerism of Quinapril and Quinaprilat by UPLC–DAD and Elucidation of the Conformational Equilibrium by NMR
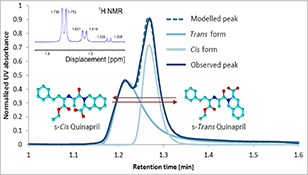
Quinapril and quinaprilat are two angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors characterized by a band broadening and a peak splitting when analyzed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography. These observations, attributed to the existence of a conformational s-cis–s-trans equilibrium, established by the rotation around the peptide bond of both products, were examined by NMR and ultra-performance liquid chromatography–diode array detector.
CH14379A Novel Electrochemiluminescence Sensor for Sensitive Determination of Carbaryl Based on Solid Phase Microextraction at NH2–Graphene–Nafion Modified Electrode
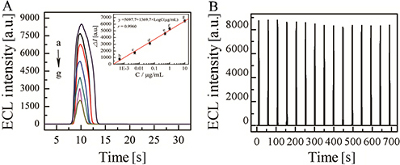
Electrochemiluminescence detection and solid phase microextraction using a NH2–graphene–Nafion modified glassy carbon electrode was developed for carbaryl with a linearity range of 5 × 10–4 to 10 μg mL–1 and a detection limit of 2 × 10–4 μg mL–1, which shows good reproducibility, stability, and precision.
CH14393Square-Wave Voltammetric Determination of Nanomolar Levels of Linuron in Environmental Water Samples Using a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Platinum Nanoparticles within a Dihexadecyl Phosphate Film
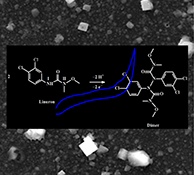
A new sensitive method for linuron determination using a glassy carbon electrode modified with platinum nanoparticles within a dihexadecyl phosphate film (PtNPs-DHP/GCE) and square-wave voltammetry was proposed.
CH14350Cationic Charged Polymer Vesicles from Amphiphilic PEI-g-PSSA-g-PEI as Potential Gene Delivery Vehicles
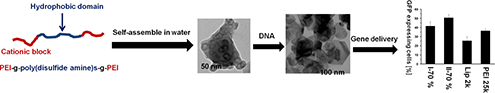
Polymer vesicles have attracted extensive interest for a variety of biomedical applications. To our knowledge, few reports focus on polymer vesicles for gene delivery. A novel library of cationic polymer vesicles with tunable hydrophobicity is evaluated as efficient and low-cytotoxicity gene vectors.
CH14073‘Green' Synthesis of 2-Substituted 6-Hydroxy-[3H]-pyrimidin-4-ones and 4,6-Dichloropyrimidines: Improved Strategies and Mechanistic Study
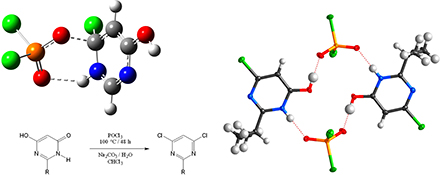
An improved route to 2-substituted 6-hydroxy-[3H]-pyrimidin-4-ones and 4,6-dichloropyrimidines using phosphoryl chloride gives yields up to 86 % on a one mol scale. Computations suggest that the chlorination occurs in an alternating phosphorylation–chlorination manner. The investigated 4,6-dichloropyrimidines form strong complexes with dichlorophosphoric acid but weak complexes with hydrochloric acid.
CH14351Design and Synthesis of Piperazine-Based Task-Specific Ionic Liquids for Liquid–Liquid Extraction of CuII, NiII, and CoII from Water
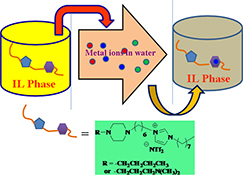
The novel task-specific ionic liquids (TSILs) introducing piperazine substructures were synthesized via a simple four-step process starting from available materials. TSILs can efficiently remove Cu2+, Ni2+, and Co2+ from water in mild acid solutions. The thermodynamics indicated that the extraction process was exothermic and spontaneous in nature.
CH14447Preparation of Metal-Free Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Via Direct Electrochemical Exfoliation of Graphite in Ammonium Nitrate
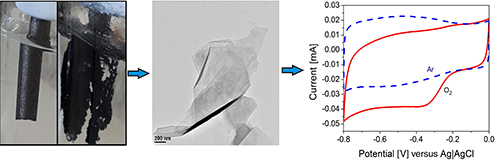
Metal-free nitrogen-doped graphene can be easily prepared by direct electrochemical exfoliation of graphite in aqueous ammonium nitrate electrolytes for use as catalysts for oxygen reduction reactions.
CH14437Novel Tri-Cholesteryl Derivatives-Based Low Molecular Mass Organic Gelators with Multi-Stimuli Responsive Properties
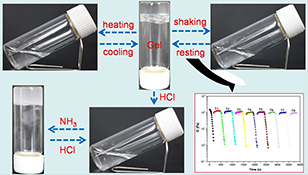
Two novel tri-cholesteryl derivatives gel several liquids at room temperature. One of the gels, 1/cyclohexane, possesses multi-stimuli responsive properties and shows super smart and reversible thixotropic property. These findings suggest that there is a big potential for developing tri-cholesteryl derivatives into extraordinary low molecular mass gelators.
CH14659An Efficient Microwave Method for the Synthesis of Imines
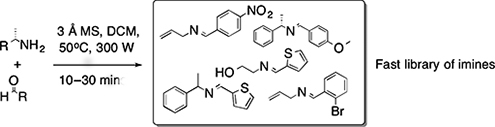
An efficient microwave synthesis of imines has been developed giving quantitative conversions, in a significantly reduced time frame and without the aid of expensive or elaborate chemicals. A large library of functionalised and unfunctionalised imines was quickly synthesised with minimal workup procedures.



