10th Anniversary Collection of RACI and AAS Award papers
Organic radical polymers are being developed for applications such as energy storage, catalysis and spintronics. Quantification of radical content can be nuanced, with a variety of techniques available for characterisation. This primer provides an overview and discusses the challenges of implementation to macromolecules containing pendant radicals. (Image credit: Theo A. Ellingsen.)
This article belongs to the 10th Anniversary Collection of RACI and AAS Award papers.
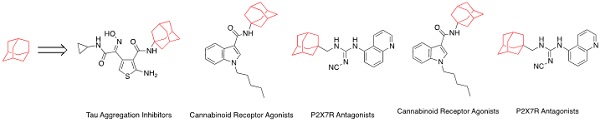
Adamantyl-containing compounds have proven to be effective ligands at a range of therapeutic targets. Its unique structural and physicochemical properties provide a promising strategy to increase lipophilicity and introduce three-dimensionality to a structure. The following Account highlights our group’s research in five drug discovery programs showcasing the use of adamantane. (Image credit: Chianna Dane.)
This article belongs to the 10th Anniversary Collection of RACI and AAS Award papers.
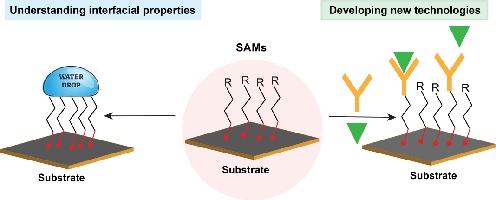
Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) allow surfaces to be modified with molecular-level control to give surface-specific functionality. SAMs have provided fundamental insight into surface phenomena and found utility in a range of applications. This account outlines a variety of different SAM systems and their application in sensing. (Image credit: Essam M. Dief.)
This article belongs to the 10th Anniversary Collection of RACI and AAS Award papers.
The nudibranch Goniobranchus coi sequesters and concentrates antifeedant oxygenated diterpenes into its mantle dermal formations to utilise as a chemical weapon when attacked by predators. Through chemical correlation, high-field NMR spectroscopy and molecular modelling new oxygenated metabolites were identified and elucidated. (Image credit: Louise C. Forster.)
This article belongs to the 10th Anniversary Collection of RACI and AAS Award papers.
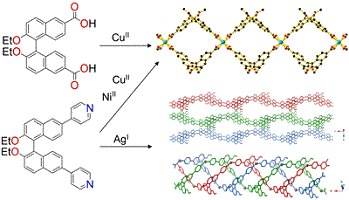
Chiral supramolecular compounds containing 1,1′-binapthyl are increasingly explored for chiroptical techniques including fluorescence-based sensing. Careful design of these compounds can yield systems with accessible voids and complimentary intermolecular interactions that can be tailored as a function of the 1,1′-binapthyl’s steric hinderance and hydrogen bonding ability. (Image credit: Carol Hua.)
This article belongs to the 10th Anniversary Collection of RACI and AAS Award papers
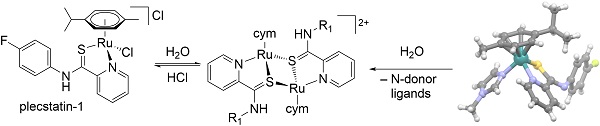
Replacing the chlorido ligand in [Ru(η6-p-cymene)(p-fluoropyridinecarbothioamide)Cl]PF6 with the N-heterocycles 1-methylimidazole, 1-methylbenzimidazole and pyridine gave complexes with similar antiproliferative activities in human cancer cells at low micromolar concentrations. This can be explained by dimerisation in aqueous solution and formation of the same di-Ru complexes after cleaving of the chlorido or N-heterocycle ligands. (Image credit: Saawan Kumar.)
This article belongs to the 10th Anniversary Collection of RACI and AAS Award papers.
The 18th century cleric Thomas Bayes gave his name to an elegant statement of the probability of an event – in this case identification of an odour – given some evidence: output from a number of metal oxide semiconductor sensors. Knowing the distributions of outputs for target odours, we assign the probabilities of an unknown odour. The greatest probability wins! (Image credit: E-nose Pty Ltd and D. B. Hibbert.)
This article belongs to the 10th Anniversary Collection of RACI and AAS Award papers.
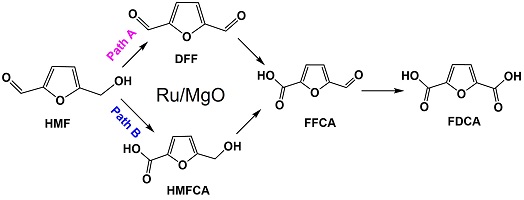
Biomass offers a sustainable alternative source of carbon to existing fossil resources that underpin the global chemical industry – on which we rely for fuels, plastics and pharmaceuticals. Combining ruthenium metal with Earth-abundant magnesium oxide creates an efficient catalyst for transforming sugar components of waste biomass into a valuable precursor for the sustainable manufacture of plastics. (Image credit: Priya Lokhande.)
This article belongs to the 10th Anniversary Collection of RACI and AAS Award papers.
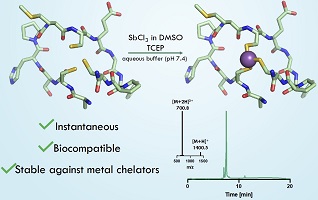
Cyclic peptide drugs are important therapeutics. Previously, bismuth and arsenic were introduced to create peptide bicycles by binding three cysteines. Now, antimony complements this set of elements to form stable bicyclic peptides. These remain stable in the presence of a common metal chelator and glutathione. Bismuth outcompetes antimony as the core atom in peptide bicycles. (Image credit: Lani Davies.)
This article belongs to the 10th Anniversary Collection of RACI and AAS Award papers.