Marine and Freshwater Research
Volume 75
Number 14 2024
Seasonal flooding promotes habitat diversity that influences biodiversity and ecological processes in river–floodplain ecosystems. We demonstrated that environmental conditions in floodplain pools on the Fitzroy River (WA) vary substantially compared with the main channel, providing an important habitat for organisms that contribute to landscape-scale ecosystem function. Floodplain pools fill a unique role in the wider river–floodplain ecosystem and should be protected from negative effects of water development.
In this study, we sought to reconstruct tropical tuna dietary histories by using different metrics of stomach fullness and to assess their association with fisheries-related, environmental and biological covariates. Our results add to the evidence that tropical tunas forage more effectively during the day and more actively when not associated with floating objects. Further research is needed to understand the factors governing this promising indicator of ecosystem change.
Coastal waters can be crucial nursery grounds for young sharks, but these areas are subject to a wide range of environmental changes and human interference. Our study found no significant effects on newborn populations of two reef shark species. This indicates either their remarkable resilience to environmental shifts and human presence in their habitats, or that these populations are historically degraded.
Modern fish-protection screens are implemented globally to conserve aquatic ecosystems and infrastructure. They safeguard up to 90% of fish from water diversions, with Australian governments investing ~A$40 million in incentive programs. Progress in New South Wales includes screening 36 pumps from 2018 to 2024, protecting over 819,000 native fish yearly and delivering cleaner water for agriculture. Challenges remain in cost management and national expansion, necessitating prioritisation, affordability, industry stewardship, and ongoing advancements towards widespread adoption.
This study examined the benthic diatom biodiversity–productivity relationship (BPRs) and the underlying mechanisms in high-plateau lakes along trophic states. The BPRs were linear and positive at all trophic levels, but eutrophication may weaken this relationship. Motile, non-attached and small-sized cells contributed notably to reducing the productivity and BPR. Nutrients affected productivity indirectly by influencing algal community structure, niche width and by biodiversity change.
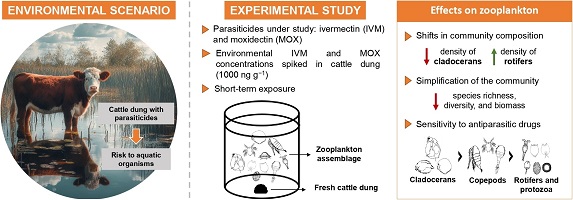
Popular antiparasitic drugs for livestock, ivermectin and moxidectin, are posing threats to aquatic ecosystems. In a brief laboratory study, we investigated their impact on zooplankton when administered through cattle dung. Results showed a disruption in zooplankton communities, with moxidectin being more toxic. These findings could have serious implications for long-term ecosystem health, emphasising the urgent need for protective measures and sustainable livestock management practices. (Image credit: Camila J. Lorente.)
This study showed the presence of juvenile olive ridley turtles in north-eastern Brazil, with 62.04% of 266 records being juveniles, including ‘lost years’ individuals up to 25.9 cm. Anthropogenic interaction with fishing (83.02%) is the main cause of strandings. The north-eastern region is vital as a habitat, necessitating continuous monitoring and conservation, particularly in heavily fished areas.
Mahseer fish, listed as Data Deficient with a decreasing population trend in The IUCN Red List, is valuable. Scientometric studies evaluate research efficacy. This study assessed mahseer research in Asia by using scientometric analysis. Analysis from Web of Science database showed a slight upward trend. Scientific publications on mahseer exhibited a significant increase. Research in Asia has potential for future scientific endeavours. The findings highlighted the importance of understanding research trends to inform conservation efforts for mahseer species in Asia.
This article belongs to the collection Ecological Monitoring and Assessment of Freshwater Ecosystems: new trends and future challenges.
Eutrophication pollution has become an important ecological problem in the world. This paper mainly analyses the current water quality of a reservoir, and on this basis, conducts an in-depth investigation and calculation of the reservoir pollution sources, evaluates the current degree of eutrophication pollution of the reservoir, and provides reference for the effective management and management of the subsequent reservoir.
This article belongs to the collection Ecological monitoring and assessment of freshwater ecosystems: new trends and future challenges.