
Australian Journal of Chemistry
Volume 71 Numbers 2 & 3 2018
CH17334A Novel Strategy to Introduce 18F, a Positron Emitting Radionuclide, into a Gallium Nitrate Complex: Synthesis, NMR, X-Ray Crystal Structure, and Preliminary Studies on Radiolabelling with 18F
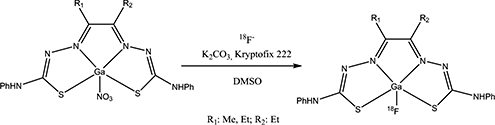
Substituted diphenyl dithiosemicarbazone gallium nitrate and fluoride complexes have been synthesised and the structures confirmed by NMR and X-ray crystallography. Radiolabelling of the nitrate complexes has been performed with fluorine-18, resulting in the formation of Ga-18F complexes.
CH17354Ultrafast NH3 Sensing Properties of WO3@CoWO4 Heterojunction Nanofibres at Room Temperature
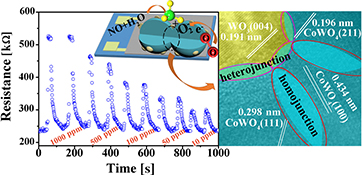
A Co-W nanofibre sensor was found to exhibit excellent gas-sensing properties at room temperature, such as a response of 1.17 and 3 s to 1000 ppm NH3, and the response time always remained within 5 s for a NH3 concentration range of 1000–10 ppm, due to the single crystal CoWO4–CoWO4 homojunctions and unique massage ball-like WO3–CoWO4 heterojunctions.
CH17341Regioselective Synthesis of 2,5-Disubstituted Pyrroles via Stepwise Iododesilylation and Coupling Reactions
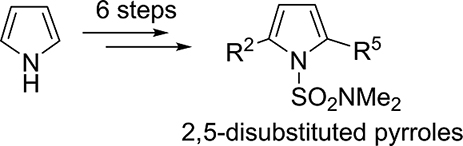
The regioselective preparation of 2,5-disubstituted pyrroles, useful structural scaffolds, is important. To this end, a protocol based on a stepwise iododesilylation and a subsequent coupling reaction, involving a 6-step pathway starting from the simplest pyrrole, has been realised. This methodology can be widely used in the synthesis of drugs, molecular wires, and high-molecular-weight polymers.
CH17472Quantum-Chemical Ab Initio Calculations on Inda- and Thallabenzene (C5H5In and C5H5Tl) and their Structural Isomers η5-C5H5In and η5-C5H5Tl
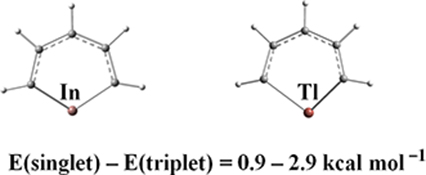
Quantum-chemical calculations were performed on the so far elusive compounds inda- and thallabenzene. The ground states of both compounds were found to be triplets with the lowest closed-shell singlets up to 3 kcal mol−1 higher in energy. The η5 isomers were found to be energetically up to 102 kcal mol−1 below the six-membered rings.
CH17498Two Coordination Polymers Constructed from Pentanuclear Zinc Clusters with Triazolate and Benzenecarboxylate Ligands: Selective Gas Adsorption
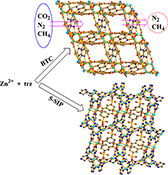
Introduction of the 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylate into the zinc-triazolate system gave the 3D porous structure of 1 based on pentanuclear [Zn5(μ3-OH)2] clusters and exhibited selective gas adsorption. While a variation of BTC3−, the 5-sulfoisophthalate was introduced into the zinc-triazolate system yielding a non-porous structure of 2 constructed from pentanuclear [Zn5(trz)8] clusters, demonstrating that the secondary ligands play an important role in the formation of the final structures.
CH17420Superoxide Anion Biosensor Based on Bionic-Enzyme Hyperbranched Polyester Particles
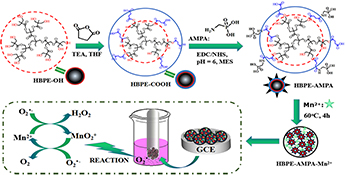
Conventionally synthesised Mn-superoxide dismutase mimics have a multilayer sheet structure with uncontrolled shape, which wastes resources and has a low catalytic efficiency. Here, a bionic-enzyme hyperbranched polyester (HBPE-AMPA-Mn2+) has been synthesised by a self-assembly technique. Results indicate that an electrochemical biosensor based on HBPE-AMPA-Mn2+ particles has excellent electrochemical performance.
CH17406Phosphate and Phosphonate-Based Ionic Liquids as New Additives in Foeniculum vulgare Essential Oil Extraction
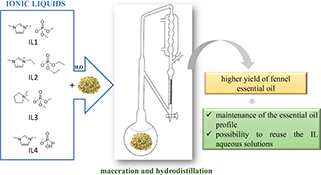
Four ionic liquids (ILs) were added separately in the essential oil extraction of Foeniculum vulgare fruits. The use of each aqueous solution of IL afforded an increase in the essential oil yield. There is possibility of reuse of the IL solutions and no variation in the fennel essential oil composition was evidenced.
CH17532Host (–)-(2R,3R)-2,3-Dimethoxy-1,1,4,4-tetraphenylbutane-1,4-diol and Guests Aniline, N-Methylaniline, and N,N-Dimethylaniline: A Selectivity Study
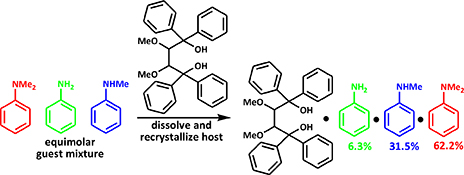
DMT ((–)-(2R,3R)-2,3-dimethoxy-1,1,4,4-tetraphenylbutane-1,4-diol) is an efficient host compound for guests aniline, N-methylaniline, and N,N-dimethylaniline. This host displays high selectivity for N,N-dimethylaniline when recrystallized from various mixtures comprising these three guests. DMT may therefore have future application in the separation of these anilines.
CH17470Rapid Determination of H2S Poisoning in a Forensic Study Using a Novel Fluorescence Assay Based on Zn/Cu@BSA Nanoclusters
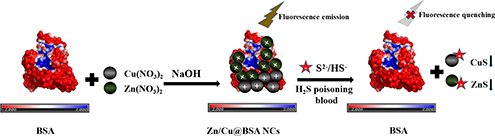
Zn/Cu@BSA nanoclusters with strong florescence were synthesised using zinc nitrate, copper nitrate, and bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a stabilising agent, and were used for the detection of H2S poisoning based on fluorescence quenching due to the formation of a metal–sulfide precipitate.
CH17411Kinetic and Computational Studies of Rhenium Catalysis for Oxygen Atom Transfer Reactions
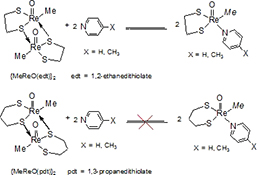
An experimental and computational study explains the reactivity difference between the oxorhenium(v) dimer {MeReO(edt)}2 (where edt = 1,2-ethanedithiolate) and the oxorhenium(v) dimer {MeReO(pdt)}2 (pdt = 1,3-propanedithiolate). The {MeReO(edt)}2 monomerization reaction is more thermodynamically favoured than that of the {MeReO(pdt)}2 due to higher angle strain on the {MeReO(edt)}2 bridging sulfur.
CH17508A Straightforward Methodology for the Synthesis of α,ω-Telechelic Poly(dimethylsiloxane)s
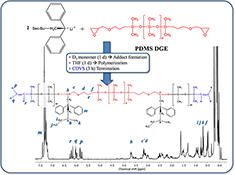
Living anionic polymerization provides one of the best approaches for synthesizing complex macromolecular structures. In this work, we report the synthesis of α,ω-telechelic poly(dimethylsiloxane)s (α,ω-PDMS) by employing a novel bifunctional initiator obtained from a commercially available siloxane precursor, diglycidylether-terminated poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS-DGE).
CH17503A Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Rapid Detection of Tetracycline Based on Ordered Mesoporous Carbon–Fe3O4
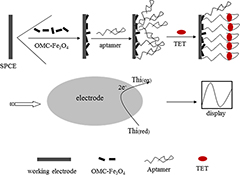
A label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on ordered mesoporous carbon–Fe3O4 modified screen-printed carbon electrode was constructed for rapid detection of tetracycline. The limit of detection of this aptasensor was 0.8 nM (S/N = 3). Furthermore, the aptasensor showed high specificity towards tetracycline, good reproducibility, and long-term stability.
CH17572Preparation and Characterization of PMMA Particles Incorporating a Chemical Sunscreen Agent for Improvement of UV Protection Ability
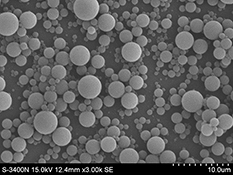
Discovering new UV filters or modifying well-known UV filters are important ways for the development of sunscreens. Encapsulating chemical sunscreen agent in PMMA particles can greatly reduce the skin irritation caused by direct contact with skin; moreover, the UV protection ability also showed a significant improvement.
CH17530Carbon Dioxide Utilisation for the Synthesis of Unsymmetrical Dialkyl and Cyclic Carbonates Promoted by Basic Ionic Liquids
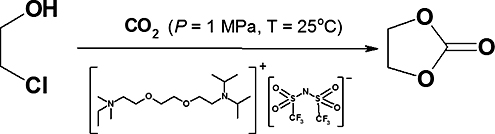
An efficient and greener synthesis of unsymmetrical and cyclic organic carbonates mediated by Hünig’s base-appended ionic liquids, via carbon dioxide conversion, is described.
CH17590Saccharin and tert-Butyl Nitrite: Cheap and Efficient Reagents for the Synthesis of 1,2,3-Benzotriazine-4-(3H)-ones from 2-Aminobenzamides under Metal-Free Conditions
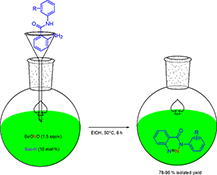
A mild and eco-friendly protocol for the synthesis of 1,2,3-benzotriazine-4-(3H)-ones is described using saccharin as a cheap and efficient catalyst and tert-butyl nitrite as a diazotization reagent for the first time. The current method has advantages such as cost effectiveness, simple experimental procedure, good yield of the desired product, and metal-free as well as environmentally benign conditions.
CH17595Cyanosilylation of Aldehydes Catalyzed by Iron(III) Arylhydrazone-β-Diketone Complexes
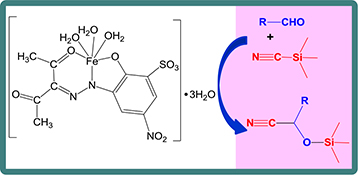
Mononuclear iron(iii)-arylhydrazone-β-diketone complexes act as homogeneous catalysts for the cyanosilylation of aldehydes with trimethylsilyl cyanide, leading to cyanohydrin trimethylsilyl ethers in methanol at room temperature.
CH17523Highly Ordered Supramolecular Nanoassemblies of Paramagnetic Amphiphilic Chelates as Potential MRI Contrast Agents
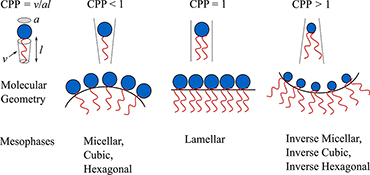
Self-assembled nanoparticles, or nanoassemblies, of paramagnetic amphiphilic chelates have high potential as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. However, due to the inherently large paramagnetic chelate as the head group (CPP <1), it is challenging to design paramagnetic amphiphiles to confer nanoassemblies with highly ordered interior nanostructures. Recent studies reporting stable, highly ordered nanoassemblies of paramagnetic amphiphilic chelates are presented here.
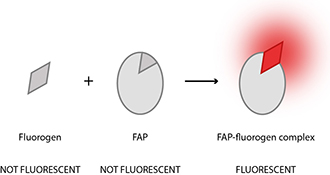
Fluorogens are new generation small molecule organic dyes that offer an alternative, rapid, and non-covalent labelling strategy. These otherwise dark molecules bind to genetically encoded recognition domains, termed fluorogen activating proteins (FAPs), causing a protein-mediated constraint of rotation of a single bond within the fluorogens, and leading to increased fluorescence as high as 20000-fold.



