The frog Aubria subsigillata is an edible species that is highly valued in the human diet in Benin. However, a strong rarefaction of the species due to its uncontrolled exploitation is observed in the wild. The 0.2 IU/g of Ovulin hormone administered intrafemorally enabled collection of gametes at 13 h in males and 27 h in females, and 172 eggs of 1 mg were incubated after 167 h. A. subsigillata reproduction goes through five phases: (1) selection of mature broodstock; (2) hormonal injection; (3) gamete collection; (4) in vitro fertilisation; and (5) incubation. Photograph by Houénafa A. C. Gansa.

Reproduction, Fertility and Development
Volume 36 Number 9 2024
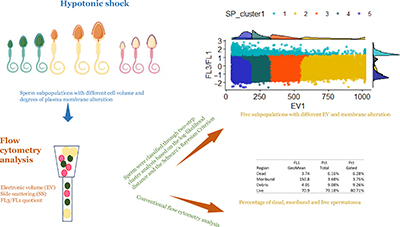
Evaluation of sperm quality in farm animals and humans is crucial to predict reproductive efficiency, yet conventional tests are not sufficient to predict fertility. Clustering sperm using individual data from flow cytometry analysis provides more information than typical dot plots, which could better predict sperm fertility and cryotolerance. Herein, combining cluster analysis with flow cytometry led to the identification of five sperm subpopulations with differences in cell volume and membrane integrity, whereas typical dot plots just allowed for the identification of three. Image by the authors.
This article belongs to the Collection Dedication to Jim Cummins.
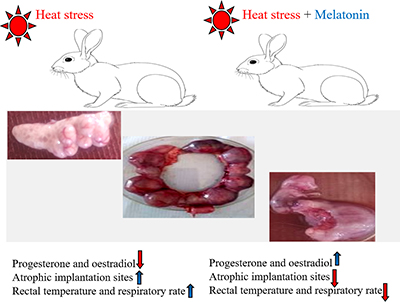
Melatonin administration (1 mg/kg body weight) during the first half of pregnancy of heat-stressed rabbits improved heat-tolerance capacity, sex hormone production, and fetal viability. These positive effects were subsequently associated with improved conception rate and kindling rate. Image by authors.
This article belongs to the Collection Non-photoperiodic Actions of Melatonin.
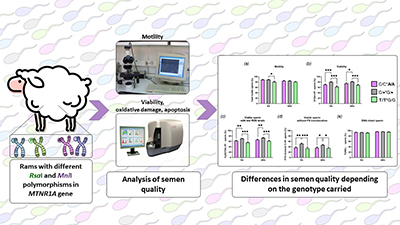
Some variants of the melatonin receptor gene affect seasonal reproduction in sheep, but it is not clear how they affect males and their spermatozoa. This study explores the impact of two genetic variants of the melatonin receptor gene on ram seminal quality throughout the year. Results revealed that there is a detrimental effect on seminal quality, more pronounced during the reproductive season, depending on the variant carried, which highlights the potential of genotyping for optimal sire selection in breeding programs. Image by Victoria Peña-Delgado.
This article belongs to the Collection Dedication to Jim Cummins.
RD23235 Abstract | RD23235 Full Text | RD23235PDF (1.8 MB) | RD23235Supplementary Material (729 KB) Open Access Article
Poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are widespread environmental contaminants that can accumulate in body tissues and cause adverse health outcomes. This article combines the perspectives of chemists, soil scientists, reproductive biologists, and health policy researchers, to summarise the issue of PFAS contamination and its specific impact on the reproductive health of all animals. It also highlights the important role scientists have to play in educating the public and policy makers on the complexity of the planetary health issues surrounding PFAS. Images were obtained from iStock: https://www.istockphoto.com/
RD24034 Abstract | RD24034 Full Text | RD24034PDF (905 KB) Open Access Article
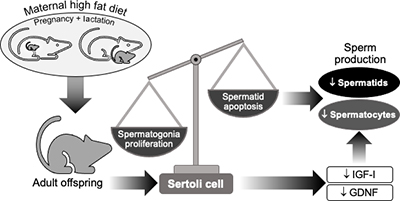
In rats, we tested whether a high-fat diet fed to mothers during pregnancy and lactation would affect Sertoli cell function in their adult offspring. Changes in transcription factors and proteins that control proliferation and apoptosis in germ cells suggest that the high-fat diet alters the balance between cell proliferation and apoptosis, potentially reducing sperm production. Image by Graciela Pedrana, Grame Martin.
RD23082 Abstract | RD23082 Full Text | RD23082PDF (6.3 MB) Open Access Article