The lipid composition depends on the mussel size; small mussels have an elevated content of main lipid classes. Bivalves have mechanisms to regulate the fatty acid composition of membrane lipids, including maintenance of a constant unsaturation degree of phospholipid fatty acids. Selective retention of arachidonic acid as well as accumulation of non-methylene-interrupted fatty acids in mussels are assumed to be biomarkers of environmental stress. Contents of minor phospholipid fractions in combination with unsaturated fatty acids can be used for monitoring of the health status of mussels.

Marine and Freshwater Research
Volume 75 Number 12 2024
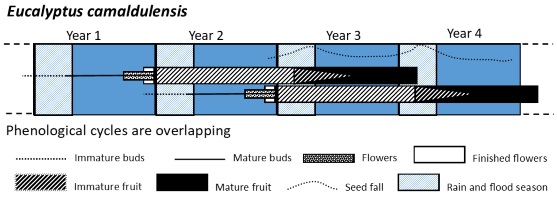
Eucalyptus camaldulensis and Eucalyptus coolabah are floodplain trees found in the Murray–Darling Basin (MDB). This long-term study observed the timing and abundance of buds, flowers and fruits at sites in the northern MDB and looked for patterns that would indicate the influence of river flows. Bud abundance, canopy seed storage and seed fall were influenced by moisture availability in both species. Image credit: J. L. Kerr.
This article belongs to the collection Environmental flows in northern Murray–Darling Basin: what we know about the science and management after a decade of practice.
MF24034 Abstract | MF24034 Full Text | MF24034PDF (1.8 MB) | MF24034Supplementary Material (1.5 MB) Open Access Article
We developed a learning approach for managing water for the environment, globally, as learning is essential for effective and successful management. This learning approach is exemplified using the Macquarie River and Marshes in the Murray–Darling Basin, Australia. To improve ongoing learning in managing water for the environment, we recommend institutionalising learning, increasing flexibility in governance arrangements, fostering social-learning capacity, and developing explicit learning understanding by nurturing learning mandates and champions.
This article belongs to the collection Environmental Flows in Northern Murray–Darling Basin: what we know about the science and management after a decade of practice.
MF24049 Abstract | MF24049 Full Text | MF24049PDF (1.9 MB) Open Access Article
The first study on the exploitation levels and aspects of biology of Halaelurus quagga, a poorly known deep-water catshark, showed a female-dominated sex ratio, a positively allometric growth in females and isometric growth in males. Mature H. quagga males ranged between 294 and 336 mm, and females between 315 and 370 mm, with pregnant females carrying two, three or four egg cases, with embryos in each uterus. This species is landed (and discarded) as bycatch in shrimp fisheries, with the catches comprising a significant amount of reproductively active individuals.
Exploring trends in rainfall across the middle and lower Yangtze River Basin from 1961 to 2022, this study showed a shift from reduced fluctuations to increased precipitation c. 2011, becoming notably pronounced after 2017. Utilising ARIMA models and expert techniques, it forecast future trends, aiding flood management and climate adaptation strategies, with implications for advanced climate modelling and data analytics.
This article belongs to the collection Ecological monitoring and assessment of freshwater ecosystems: new trends and future challenges.
The depth use of young porbeagles was investigated for the first time during the summer and autumn in the north-western Atlantic. Depth use varied on both daily and seasonal scales, with sharks occupying surface waters during the night and summer, and diving deeper during the day and autumn. Results can inform bycatch reduction strategies for this vulnerable life stage.
We conducted a microplastics survey in a stretch of the Paraíba do Sul River basin, the water system of which flows through the most populous area in Brazil. Samples were taken from the superficial layer of the water column during the Carnival period in 2023. Higher microplastic concentrations were observed after the Carnival event than in the pre- and during-Carnival periods.