FLUXY: a simple code for computing steady-state metal fluxes at consuming (bio)interfaces, in natural waters
Zeshi Zhang A , Jacques Buffle A B , Konstantin Startchev A and Davide Alemani AA Analytical and Biophysical Environmental Chemistry (CABE), University of Geneva, Sciences II, 30 quai E. Ansermet, 1211 Geneva 4, Switzerland.
B Corresponding author. Email: jacques.buffle@cabe.unige.ch
Environmental Chemistry 5(3) 204-217 https://doi.org/10.1071/EN07095
Submitted: 20 December 2007 Accepted: 7 April 2008 Published: 19 June 2008
Environmental context. Until now there was no user-friendly code for metal flux computations in natural mixtures of aquatic complexants, which are however essential for prediction of metal bioavailability. The present paper describes the capabilities and limitations of one of the only two such codes presently available, called FLUXY. The results of FLUXY are compared with those of another code, and it is shown that it enables quick computation and is applicable to natural ligands under many environmental conditions.
Abstract. The computation of metal fluxes at consuming interfaces like microorganisms or bioanalogical sensors is of great importance in ecotoxicology. The present paper describes the application of a simple code, FLUXY, for the computation of steady-state metal fluxes in the presence of a very large number of complexes, with broadly varying values of equilibrium constants, rate constants and diffusion coefficients. This code includes two major limiting assumptions, namely, (i) the existence of excess of ligand (L) compared with metal (M), and (ii) the fact that in a series of successive MLn complexes, the reaction 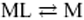 is the rate-limiting step in flux computation. The domains of rate constants for which these assumptions are valid are tested systematically, and the corresponding errors are evaluated by comparison with the exact results given by another code: MHEDYN. FLUXY is then applied and compared with MHEDYN for case studies typical of aquatic systems, namely (i) a culture medium containing simple ligands; (ii) solutions of fulvic compounds including a broad distribution of complex stability and rate constants; and (iii) suspensions of aggregates with a broad size distribution. It is shown that FLUXY gives good results for cases (i) and (iii). Application to case (ii) (fulvic compounds) is also feasible under conditions that are clearly described. Altogether, FLUXY and MHEDYN are complementary. In particular, FLUXY only computes steady-state fluxes and requires the fulfilment of a few conditions, but when these are met, computations require much less computer time than MHEDYN.
is the rate-limiting step in flux computation. The domains of rate constants for which these assumptions are valid are tested systematically, and the corresponding errors are evaluated by comparison with the exact results given by another code: MHEDYN. FLUXY is then applied and compared with MHEDYN for case studies typical of aquatic systems, namely (i) a culture medium containing simple ligands; (ii) solutions of fulvic compounds including a broad distribution of complex stability and rate constants; and (iii) suspensions of aggregates with a broad size distribution. It is shown that FLUXY gives good results for cases (i) and (iii). Application to case (ii) (fulvic compounds) is also feasible under conditions that are clearly described. Altogether, FLUXY and MHEDYN are complementary. In particular, FLUXY only computes steady-state fluxes and requires the fulfilment of a few conditions, but when these are met, computations require much less computer time than MHEDYN.
Additional keywords: aggregate complexes, calculations, dynamic speciation, fulvic complexes, ligand excess, ligand mixtures, successive metal complexes.
Acknowledgements
The present work was initiated during sabbatical leave of J. Buffle in the Centre for Advanced Analytical Chemistry, at CSIRO. J. B. thanks G. Batley and S. Apte for stimulating discussions. The work was partly supported by the EU project ECODIS (No. 518043).
[1]
[2]
J. Buffle ,
M.-L. Tercier-Waeber ,
Voltammetric environmental trace-metal analysis and speciation: from laboratory to in situ measurements.
Trend. Anal. Chem. 2005
, 24, 172.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[3]
H. P. Van Leeuwen ,
R. M. Town ,
J. Buffle ,
R. Cleven ,
W. Davison ,
J. Puy ,
W. H. van Riemsdijl ,
L. Sigg ,
Dynamic speciation analysis and bioavailability of metals in aquatic systems
Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005
, 39, 8545.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[4]
J. Buffle ,
Z. Zhang ,
K. Startchev ,
Metal flux and dynamic speciation at (bio)interfaces. Part I: Critical evaluation and compilation of physico-chemical parameters for complexes with simple ligands and fulvic/humic substances.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007
, 41, 7609.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[5]
Z. Zhang ,
J. Buffle ,
D. Alemani ,
Metal flux and dynamic speciation at (bio)interfaces. Part II: Evaluation and compilation of physico-chemical parameters for complexes with particles and aggregates.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007
, 41, 7621.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[6]
[7]
C. Fortin ,
P. G. C. Campbell ,
Silver uptake by the green alga Chlamydomonas rheinhardtii in relation to speciation: the role of chloride.
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000
, 19, 2769.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[8]
[9]
[10]
J. Koutecky ,
J. Koryta ,
The general theory of polarographic kinetic currents.
Electrochim. Acta 1961
, 3, 318.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[11]
Z. Zhang ,
J. Buffle ,
H. P. van Leeuwen ,
Roles of dynamic metal speciation and membrane permeability in metal flux through lipophilic membranes: general theory and experimental validation with non-labile complexes.
Langmuir 2007
, 23, 5216.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[12]
J. Salvador ,
J. Puy ,
J. Cecilia ,
J. Galceran ,
Lability of complexes in steady-state finite planar diffusion.
J. Electroanal. Chem. 2006
, 588, 303.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[13]
J. Salvador ,
J. L. Garcés ,
E. Companys ,
J. Cecilia ,
J. Galceran ,
J. Puy ,
R. M. Town ,
Ligand mixture effects in metal complex lability.
J. Phys. Chem. A 2007
, 111, 4304.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[14]
J. Galceran ,
J. Puy ,
J. Salvador ,
J. Cecilia ,
F. Mas ,
J. L. Garces ,
Lability and mobility effects on mixtures of ligands under steady-state conditions.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003
, 5, 5091.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[15]
J. Salvador ,
J. L. Garces ,
J. Galceran ,
J. Puy ,
Lability of a mixture of metal complexes under steady-state planar diffusion in a finite domain.
J. Phys. Chem. B 2006
, 110, 13661.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[16]
J. Puy ,
J. Cecilia ,
J. Galceran ,
R. M. Town ,
H. P. van Leeuwen ,
Voltammetric lability of multiligand complexes: the case of ML2.
J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004
, 571, 121.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[17]
J. Salvador ,
J. Puy ,
J. Galceran ,
J. Cecilia ,
R. M. Town ,
H. P. van Leeuwen ,
Lability criteria for successive metal complexes in steady-state planar diffusion.
J. Phys. Chem. B 2006
, 110, 891.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[18]
J. Buffle ,
K. Startchev ,
J. Galceran ,
Computing steady-state metal flux at microorganism and bioanalogical sensor interfaces in multiligand systems. A reaction layer approximation and its comparison with the rigorous solution.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007
, 9, 2844.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[19]
D. Alemani ,
J. Buffle ,
Z. Zhang ,
J. Galceran ,
B. Chopard ,
Metal flux and dynamic speciation at (bio)interfaces. Part III: MHEDYN, a general code for metal flux computation; application to simple and fulvic complexants.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008
, 42, 2021.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[20]
D. Alemani ,
J. Buffle ,
Z. Zhang ,
J. Galceran ,
B. Chopard ,
Metal flux and dynamic speciation at (bio)interfaces. Part IV: MHEDYN, a general code for metal flux computation; application to particulate complexants and their mixtures with the other natural ligands.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008
, 42, 2028.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[21]
F. M. M. Morel ,
J. G. Ruter ,
Aquil: a chemically defined phytoplankton culture medium for trace metal studies.
J. Phycol. 1979
, 15, 135.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[22]
D. Alemani ,
B. Chopard ,
J. Galceran ,
J. Buffle ,
LBGK method coupled to time splitting technique for solving reaction–diffusion processes in complex systems.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005
, 7, 3331.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[23]
D. Alemani ,
B. Chopard ,
J. Galceran ,
J. Buffle ,
Two grid refinement methods in the lattice Boltzmann framework for reaction–diffusion processes in complex systems.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006
, 8, 4119.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |

[24]
[25]
[26]
[27]
K. W. Bruland ,
Complexation of zinc by natural organic ligands in the central North Pacific.
Limnol. Oceanogr. 1989
, 34, 269.

[28]
[29]
J. R. Lead ,
K. W. Wilkinson ,
E. Balnois ,
B. J. Cutak ,
C. R. Larive ,
S. Assemi ,
R. Beckett ,
Diffusion coefficients and polydispersities of Suwanee River fulvic acids: comparison of fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, pulse-field gradient nuclear magnetic resonance, and flow-field-flow fractionation.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000
, 34, 3508.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[30]
J. Buffle ,
R. S. Altmann ,
M. Filella ,
A. Tessier ,
Complexation by natural heterogeneous compounds: site occupation distribution functions, a normalized description of metal complexation.
Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990
, 54, 1535.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[31]
R. S. Altmann ,
J. Buffle ,
The use of differential equilibrium functions for interpretation of metal binding in complex ligand systems: its relation to site occupation and site affinity distributions.
Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988
, 52, 1505.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[32]
J.-P. Pinheiro ,
A. M. Mota ,
M. L. Simoes-Gonçalves ,
Complexation study of humic acids with cadmium(II) and lead(II).
Anal. Chim. Acta 1994
, 284, 525.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[33]
D. Kinniburgh ,
W. H. van Riemsdijk ,
L. K. Koopal ,
M. Borkovec ,
M. F. Benedetti ,
M. J. Avena ,
Ion binding to natural organic matter: competition, heterogeneity, stoichiometry and thermodynamic consistency.
Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999
, 151, 147.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[34]
J. Buffle ,
R. S. Altmann ,
M. Filella ,
The effect of physico-chemical heterogeneity of natural complexants. Part II. The buffering action of their background sites.
Anal. Chim. Acta 1990
, 232, 225.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[35]
R. Sips ,
The structure of a catalyst surface II.
J. Chem. Phys. 1950
, 18, 1024.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

[36]
[37]
[38]
[39]
J. P. Pinheiro ,
M. Minor ,
H. P. van Leeuwen ,
Metal speciation dynamics in colloidal ligand dispersions.
Langmuir 2005
, 21, 8635.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | PubMed |



