344 PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY ACTIVITY CONTROLS NUCLEAR MATURATION OF PORCINE OOCYTES
L. Tubman A , A. Peter B and R. Krisher CA School of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University
B Department of Clinical Sciences, Purdue University
C Department of Animal Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 18(2) 279-280 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv18n2Ab344
Published: 14 December 2005
Abstract
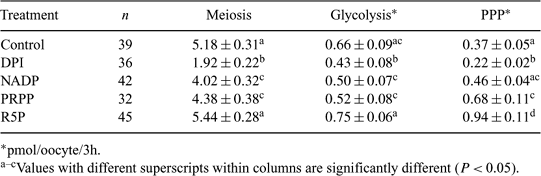
Diphenyleneiodonium (DPI), an inhibitor of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), arrests nuclear maturation of porcine oocytes. This inhibition is reversed using products or cofactors of PPP such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), phosphoribose diphosphate (PRPP), and ribose-5-phosphate (R5P). The objective of this study was to determine the relationship between DPI-mediated meiotic inhibition, reversal of this inhibition, and metabolism of in vitro-matured (IVM) porcine oocytes. Oocytes were aspirated, searched, and selected in the presence of DPI, with the exception of control oocytes. Oocytes were then matured in one of five treatments for 40 h in 7% CO2 in air at 39°C in defined Purdue Porcine Medium for maturation (PPMmat). Treatments included control, 50 nM DPI (DPI), DPI + 5 mM NADP (NADP), DPI + 12.5 mM PRPP (PRPP), and DPI + 10 mM R5P (R5P). Following IVM, oocytes were denuded by vortexing. Glycolysis and PPP activities were measured in 4 μL hanging drops containing labeled glucose (0.0125 mM 5-3H glucose and 0.482 mM 1-14C glucose, respectively) for 3 h in 6% CO2. Oocytes were then individually fixed in a 3:2:1 solution of ethanol:acetic acid:chloroform and stained with aceto-orcein for determination of meiotic stage (germinal vesicle = 1 through metaphase II = 7). Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA. The use of DPI inhibited PPP and nuclear maturation; additionally glycolysis was decreased by DPI compared to control. Addition of NADP and PRPP increased both metabolic pathways and nuclear maturation compared to DPI. R5P restored glycolysis and nuclear maturation to control levels, and PPP to above the control level. There were no significant differences among meiotic stages relative to glycolytic activity. PPP activity was significantly different (values with different superscripts; P < 0.05) among oocytes of different meiotic stages (germinal vesicle = 0.24 ± 0.03ad, germinal vesicle breakdown = 0.40 ± 0.05bcde, condensed chromatin = 0.44 ± 0.05bcd, metaphase I = 0.45 ± 0.12abcd, anaphase = 0.76 ± 0.50abcde, telophase = 0.92 ± 0.17be, metaphase II = 0.74 ± 0.08be). Percentages of oocytes reaching MII were 43.48 (control), 2.08 (DPI), 28.30 (NADP), 18.18 (PRPP), and 46.94 (R5P). These results demonstrate that the PPP is a critical control mechanism for nuclear maturation of porcine oocytes, as inhibition of this metabolic pathway resulted in arrest of nuclear maturation. Addition of PPP cofactors or end products to the arresting medium led to reversal of inhibition as demonstrated by restoration of PPP activity resulting in nuclear maturation.
|


