Transmission of human cytomegalovirus via breastmilk and potential risks to very preterm infants
Klaus Hamprecht A and Rangmar Goelz BA Institute of Medical Virology
University Hospital of Tuebingen
Elfriede Aulhorn-Str 6
72076 Tuebingen, Germany
Tel: +49 7071 2984657
Fax: +49 7071 295552
Email: klaus.hamprecht@med.uni-tuebingen.de
B Department of Neonatology
University Children’s Hospital
Calwerstr. 7
72076 Tuebingen, Germany
Tel: +49 7071 298 08 95
Fax: +49 7071 29 39 69
Email: Rangmar.Goelz@med.uni-tuebingen.de
Microbiology Australia 36(4) 190-193 https://doi.org/10.1071/MA15066
Published: 27 October 2015
Breastfeeding has clear short-term benefits for the baby1. Additionally, based on a prospective long-term cohort study from Brazil, breastfeeding is associated with improved IQ scores and increased educational attainment 30 years later2. During lactation, mother-to-infant transmission of viral infections like HIV, hepatitis B (HBV), and human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), may occur. The article presented here will focus on the dynamics of HCMV shedding into breastmilk, describe the short- and long-term risks of HCMV infection of small preterm infants, and options for prevention.
HCMV reactivation during lactation
HCMV, a β-herpesvirus, persists following primary infection for lifetime in hematopoetic CD34+ precursor cells and may be reactivated by stress, transient loss of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell immunity, IL-6 signalling, cell cycle arrest, and DNA damage3. Interestingly, HCMV is also reactivated in healthy immunocompetent seropositive women during lactation4. The ratio of HCMV reactivation at any stage of breastfeeding during the first three months after birth is very high (>95%) and nearly equals the maternal seroprevalence5,6. The mechanisms leading to viral shedding exclusively into breastmilk are not understood. HCMV seroprevalences in Western Europe, USA, Canada, and Australia range from 40–60%, and are above 90% in South Africa, Brazil, India, Japan, and Turkey7.
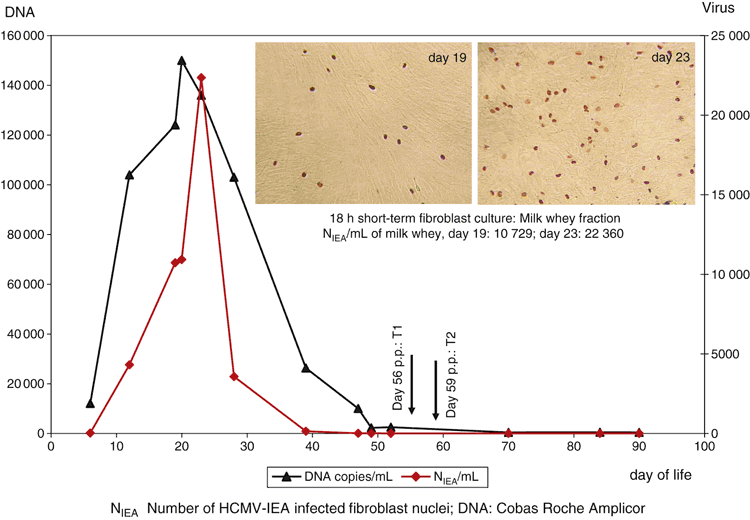
Maternal HCMV reactivation of seropositive mothers during lactation with shedding of viral DNA and virolactia8 can be detected already in colostrum and normally ends after about three months after birth. According to our experience with individual kinetics of HCMV reactivation in breastmilk of more than 500 healthy HIV-negative breastfeeding mothers of preterm infants, the onset of viral shedding begins with low viral load (<1000 copies/mL) and low infectivity (without detectable infected fibroblast nuclei in short-term microculture) at the end of the first week post partum (p.p.). The onset, the dynamics, and the end of virus shedding into milk is inter-individually different and describes mostly unimodal kinetics (Fig. 1). The viral reactivation during lactation is a strictly self-limited process8. Using overnight microculture from cell- and fat-free milk whey, virolactia peaks coincide with viral DNA peak values, varying from 103–106 copies HCMV DNA/mL of milk whey9. The initiation of viral shedding into colostrum shows divergent results. While in Gambia HCMV excretion in colostrum and genital tract were observed in 100% of congenitally infected, and 48% of early infected infants10, a study from Japan showed, that in seven cases of very low birthweight (VLBW) infants the initial viral load in breastmilk in the first week p.p. ranges between 10 and <1000 copies/mL HCMV DNA11. In contrast, an Italian group detected viral DNA in 31 out of 57 (54%) colostrum samples12.
The HCMV reactivation of HIV-negative mothers during lactation is a local process without detection of a disseminated or compartmentalised infection in plasma, throat or cervical swabs13–15. Therefore, HCMV DNA, viral late pp67 transcripts and virions can only be detected in breastmilk cells and cell-free milk whey8,9,16,17. Viral cells involved in HCMV reactivation include CD14+ macrophages9. However, HCMV-infected milk cells are not essential for virus transmission8,15. Several reports found an association between high HCMV viral load in breastmilk and risk of transmission18,19. However, other observations seem to be important in the context of prevention11. An inverse correlation between milk HCMV-specific IgG avidity and HCMV load was also found20.
In HIV/HCMV coinfected breastfeeding mothers many of the findings in the HIV-negative population are altered. Shedding of HCMV and potentially Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) in breastmilk is associated with HIV-1 transmission by breastfeeding21. About 5% of HIV-1-positive breastfeeding mothers had detectable HCMV DNA perinatally in plasma. There was a strong correlation between cervical HCMV DNA detection during pregnancy and later breast milk HCMV levels. Maternal HCMV DNA breastmilk levels and CD4 <450 cells/mm3 were determinants of HCMV transmission22. All HIV-1-infected inocula like genital secretions, breastmilk and blood contain cell-free virus and infected cells23.
Postnatal HCMV infection of very preterm infants: neonatal entity and prevention
Sepsis-like symptoms (SLS) have been introduced as a term to describe symptomatic postnatal HCMV disease in VLBW preterm infants, comprising apnea and bradycardia, hepatosplenomegaly, grey pallor and distending bowels24,25. Following maternal HCMV reactivation and shedding into BM (in 96% of seropositive mothers), the incidence of HCMV transmission to the infant feeding raw, untreated breastmilk was 38% at the age of 3 months corrected age, 18% of the infants had one or more SLS5. Virological data could be almost exactly confirmed by a recent report6 and clinical findings of postnatal CMV infection by many other studies worldwide26. The main risks for symptomatic neonatal disease are extremely low birthweight, early transmission, low GA and low infantile IgG titers27–29. In a controlled study VLBW preterm infants had a significantly higher incidence of thrombocytopenia, neutropenia and slightly increased C-reactive protein (10–20 mg/L) than matched controls. For the first time in this study clinical parameters could be confined to the entity of postnatal CMV infection in preterm infants (but additional prospective studies with standardized protocols are warranted). All additional parameters included were self-limiting and there was no impact on neonatal outcome parameters like intracranial hemorrhage, periventricular leucomalacia, retinopathy of prematurity and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)30. However, a large number of cases and case series – including a case from our department which was observed later on – describe severe illness in VLBW infants including pneumonia requiring artificial ventilation, hepatitis and gastrointestinal involvement, with some infants needing antiviral treatment with (val)ganciclovir11,26,28,31–37.
Options for prevention of virus transmission
Effective prevention of HCMV transmission is only possible through heat treatment of BM. Both long-term (30 min, 63°C) and short-term (5 s, 62°C) pasteurisation methods are effective, but short-term pasteurisation conserves nutritional and immunological relevant components in milk like HCMV-specific antibodies and enzymes38,39, while Holder pasteurisation does not. Using this method the benefits of BM feeding can be preserved without the disadvantages of CMV transmission.
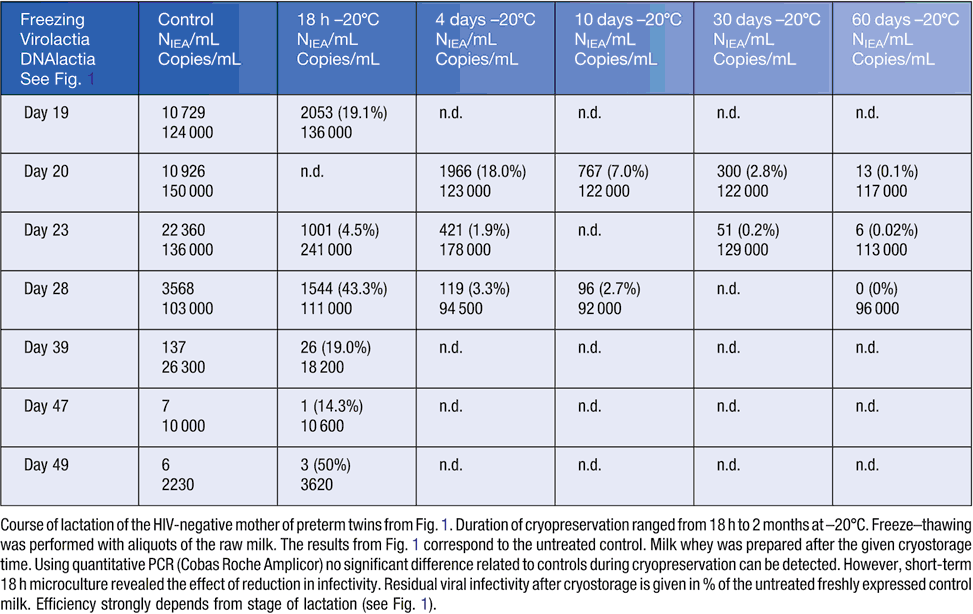
Freeze–thawing at –20°C for time intervals ranging from 18 h to 10 days is not efficient in viral elimination38,40,41. Extended duration of cryopreservation of native breast milk at –20°C from 18 h to 60 days is not efficient for complete virus killing (see Table 1) during decrease of viral DNAlactia and virolactia from peak level to baseline viral shedding, as shown in Fig. 1.
|
Long-term outcome
An earlier study revealed a significant association of postnatal HCMV infection in infants with birthweight <2000 g and neurologic sequelae and handicaps at 3 years of age42. In a more recent study, there was no difference in the neurodevelopmental outcome between VLBW infants with postnatal HCMV infection acquired during their stay in the neonatal intensive care unit and their matched controls at the age of 2–4 years43. However, this changed at the age of 4–10 years and 11–16 years: the cognitive outcome of the HCMV infected infants was significantly lower than their controls using K-ABC and HAWIK, the latter with a difference of 93 v. 103 (P < 0.03)44–46.
Summary
In conclusion, there is a relevant entity of postnatally acquired symptomatic CMV infection and disease of very preterm infants through raw breastmilk. Actual data are supporting negative influence on long-term cognitive development. Concerning prevention, only heat-inactivation is effective and short-term heat-inactivation preserves the nutritional and immunological capacity of breast milk39.
References
[1] American Academy of Pediatrics (2012) Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 129, e827–e841.| Breastfeeding and the use of human milk.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 22371471PubMed |
[2] Victora, C.G. et al. (2015) Association between breastfeeding and intelligence, educational attainment, and income at 30 years of age: a prospective cohort study from Brazil. Lancet Glob. Health 3, e199–e205.
| Association between breastfeeding and intelligence, educational attainment, and income at 30 years of age: a prospective cohort study from Brazil.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25794674PubMed |
[3] Goodrum, F. et al. (2012) Human cytomegalovirus persistence. Cell. Microbiol. 14, 644–655.
| Human cytomegalovirus persistence.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:CAS:528:DC%2BC38XmsVarur4%3D&md5=6f8fc35dfb578fc32ea8f1aefbed6857CAS | 22329758PubMed |
[4] Stagno, S. et al. (1980) Breast milk and the risk of cytomegalovirus infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 302, 1073–1076.
| Breast milk and the risk of cytomegalovirus infection.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:STN:280:DyaL3c7msFeksA%3D%3D&md5=93c731fee6ff38ddcc3b508dd9599018CAS | 6245360PubMed |
[5] Hamprecht, K. et al. (2001) Epidemiology of transmission of cytomegalovirus from mother to preterm infant by breastfeeding. Lancet 357, 513–518.
| Epidemiology of transmission of cytomegalovirus from mother to preterm infant by breastfeeding.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7lt1ShtQ%3D%3D&md5=b97a586c768d5018b3d7388b31c7ca16CAS | 11229670PubMed |
[6] Meier, J. et al. (2005) Human cytomegalovirus reactivation during lactation and mother-to-child transmission in preterm infants. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43, 1318–1324.
| Human cytomegalovirus reactivation during lactation and mother-to-child transmission in preterm infants.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 15750102PubMed |
[7] Manicklal, S. et al. (2013) The ‘silent’ global burden of congenital cytomegalovirus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 26, 86–102.
| The ‘silent’ global burden of congenital cytomegalovirus.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:CAS:528:DC%2BC3sXntVyms7w%3D&md5=67d112e96f469983b3480909f453423cCAS | 23297260PubMed |
[8] Hamprecht, K. et al. (2003) Rapid detection and quantification of cell free cytomegalovirus by a high-speed centrifugation-based microculture assay: comparison to longitudinally analyzed viral DNA load and pp67 late transcript during lactation. J. Clin. Virol. 28, 303–316.
| Rapid detection and quantification of cell free cytomegalovirus by a high-speed centrifugation-based microculture assay: comparison to longitudinally analyzed viral DNA load and pp67 late transcript during lactation.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnslSqsrs%3D&md5=a0d7b87ac7b15807ba2a712dea90d83dCAS | 14522069PubMed |
[9] Maschmann, J. et al. (2015) Characterization of human breast milk leukocytes and their potential role in cytomegalovirus transmission to newborns. Neonatology 107, 213–219.
| Characterization of human breast milk leukocytes and their potential role in cytomegalovirus transmission to newborns.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:CAS:528:DC%2BC2MXlvFeltr4%3D&md5=3aa80e5e49e3abc5a12a994c13c13022CAS | 25675905PubMed |
[10] Kaye, S. et al. (2008) Virological and immunological correlates of mother-to-child transmission of cytomegalovirus in The Gambia. J. Infect. Dis. 197, 1307–1314.
| Virological and immunological correlates of mother-to-child transmission of cytomegalovirus in The Gambia.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 18422443PubMed |
[11] Wakabayashi, H. et al. (2012) Low HCMV DNA copies can establish infection and result in significant symptoms in extremely preterm infants: a prospective study. Am. J. Perinatol. 29, 377–382.
| Low HCMV DNA copies can establish infection and result in significant symptoms in extremely preterm infants: a prospective study.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 22307845PubMed |
[12] Chiavarini, M. et al. (2011) Breastfeeding and transmission of cytomegalovirus to preterm infants. Case report and kinetic of CMV-DNA in breast milk. Ital. J. Pediatr. 37, 6.
| Breastfeeding and transmission of cytomegalovirus to preterm infants. Case report and kinetic of CMV-DNA in breast milk.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 21247481PubMed |
[13] Mosca, F. et al. (2001) Transmission of cytomegalovirus. Lancet 357, 1800.
| Transmission of cytomegalovirus.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mzktl2nuw%3D%3D&md5=fd3261776ebbc882a84bc16060adf0b7CAS | 11407383PubMed |
[14] Numazaki, K. (2001) Transmission of cytomegalovirus. Lancet 357, 1799–1800.
| Transmission of cytomegalovirus.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mzktl2nug%3D%3D&md5=40ce8d318b61d59c64dab3015856d527CAS | 11407382PubMed |
[15] Hamprecht, K. et al. (2003) Transmission of cytomegalovirus to preterm infants by breastfeeding. In New Aspects of CMV-related Immunopathology (Prösch, S., Cinatl, J., Scholz, M., eds), Vol 24, pp. 43–52, Monogr Virol, Basel, Karger.
[16] Hamprecht, K. et al. (1998) Detection of cytomegaloviral DNA in human milk cells and cell free milk whey by nested PCR. J. Virol. Methods 70, 167–176.
| Detection of cytomegaloviral DNA in human milk cells and cell free milk whey by nested PCR.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXitVKhtbs%3D&md5=869d6f446685bea0f82aa6dc1cbdb717CAS | 9562410PubMed |
[17] Hamprecht, K. et al. (2000) Transmission of cytomegalovirus infection through breast milk in term and preterm infants. The role of cell free milk whey and milk cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 478, 231–239.
| Transmission of cytomegalovirus infection through breast milk in term and preterm infants. The role of cell free milk whey and milk cells.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mrks1CqtA%3D%3D&md5=e17a2f29f2e056d4c3f0a183bc50b98eCAS | 11065076PubMed |
[18] van der Strate, B.W.A. et al. (2001) Viral load in breast milk correlates with transmission of human cytomegalovirus to preterm neonates, but lactoferrin concentrations do not. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 8, 818–821.
| 1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mzps1Cqsg%3D%3D&md5=2a4e91a500408ba092e9a1c5bd937488CAS |
[19] Jim, W.T. et al. (2009) High cytomegalovirus load and prolonged virus excretion in breast milk increase risk for viral acquisition by very low birth weight infants. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 28, 891–894.
| High cytomegalovirus load and prolonged virus excretion in breast milk increase risk for viral acquisition by very low birth weight infants.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19687768PubMed |
[20] Ehlinger, E.P. et al. (2011) Maternal cytomegalovirus-specific immune responses and symptomatic postnatal cytomegalovirus transmission in very low-birth-weight preterm infants. J. Infect. Dis. 204, 1672–1682.
| Maternal cytomegalovirus-specific immune responses and symptomatic postnatal cytomegalovirus transmission in very low-birth-weight preterm infants.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:CAS:528:DC%2BC3MXhtlyqt7jO&md5=5f5bb508580b2863f3262cb942dc6588CAS | 21984738PubMed |
[21] Viljoen, J. et al. (2015) Cytomegalovirus, and possibly Epstein–Barr virus, shedding in breast milk is associated with HIV-1 transmission by breastfeeding. AIDS 29, 145–153.
| Cytomegalovirus, and possibly Epstein–Barr virus, shedding in breast milk is associated with HIV-1 transmission by breastfeeding.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25535751PubMed |
[22] Slyker, J. et al. (2014) Compartmentalized cytomegalovirus replication and transmission in the setting of maternal HIV-1 infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 58, 564–572.
| Compartmentalized cytomegalovirus replication and transmission in the setting of maternal HIV-1 infection.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:CAS:528:DC%2BC2cXhvVSgurk%3D&md5=10f1cdcbd2910791bdbe6f7c2f86e1c1CAS | 24192386PubMed |
[23] Sagar, M. (2014) Origin of the transmitted virus in HIV infection: infected cells versus cell-free virus. J. Infect. Dis. 210, S667–S673.
| Origin of the transmitted virus in HIV infection: infected cells versus cell-free virus.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25414422PubMed |
[24] Ballard, R.A. et al. (1979) Acquired cytomegalovirus infection in preterm infants. Am. J. Dis. Child. 133, 482–485.
| 1:STN:280:DyaE1M7mt1Gqtg%3D%3D&md5=dc75fe96bc9f6a4759b0a0fa65aaf376CAS | 219685PubMed |
[25] Vochem, M. et al. (1998) Transmission of cytomegalovirus to preterm infants through breast milk. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 17, 53–58.
| Transmission of cytomegalovirus to preterm infants through breast milk.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:STN:280:DyaK1c7ivFaqug%3D%3D&md5=4d7903d2aea0b7d651dd17e3d168781bCAS | 9469396PubMed |
[26] Hamprecht, K. et al. (2008) Cytomegalovirus transmission to preterm infants during lactation. J. Clin. Virol. 41, 198–205.
| Cytomegalovirus transmission to preterm infants during lactation.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 18243784PubMed |
[27] Maschmann, J. et al. (2001) Cytomegalovirus infection of extremely low-birth weight infants via breast milk. Clin. Infect. Dis. 33, 1998–2003.
| Cytomegalovirus infection of extremely low-birth weight infants via breast milk.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MnmsFGltA%3D%3D&md5=e9e888f77225a5552edd739ae89534a1CAS | 11712092PubMed |
[28] Mehler, K. et al. (2014) High rate of symptomatic cytomegalovirus infection in extremely low gestational age preterm infants of 22–24 weeks’ gestation after transmission via breast milk. Neonatology 105, 27–32.
| High rate of symptomatic cytomegalovirus infection in extremely low gestational age preterm infants of 22–24 weeks’ gestation after transmission via breast milk.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:CAS:528:DC%2BC3sXitVShs7jL&md5=6ce7349adcf640876c8b1cc82736994fCAS | 24247027PubMed |
[29] Nijman, J. et al. (2013) Maternal and neonatal anti-cytomegalovirus IgG level and risk of postnatal cytomegalovirus transmission in preterm infants. J. Med. Virol. 85, 689–695.
| Maternal and neonatal anti-cytomegalovirus IgG level and risk of postnatal cytomegalovirus transmission in preterm infants.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 23296599PubMed |
[30] Neuberger, P. et al. (2006) Case-control study of symptoms and neonatal outcome of human milk-transmitted cytomegalovirus infection in premature infants. J. Pediatr. 148, 326–331.
| Case-control study of symptoms and neonatal outcome of human milk-transmitted cytomegalovirus infection in premature infants.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 16615961PubMed |
[31] Takahashi, R. et al. (2007) Severe postnatal cytomegalovirus infection in a very premature infant. Neonatology 92, 236–239.
| Severe postnatal cytomegalovirus infection in a very premature infant.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 17570943PubMed |
[32] Hamele, M. et al. (2010) Severe morbidity and mortality with breast milk associated cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 29, 84–86.
| Severe morbidity and mortality with breast milk associated cytomegalovirus infection.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19884873PubMed |
[33] Lanzieri, T.M. et al. (2013) Breast milk-acquired cytomegalovirus infection and disease in VLBW and premature infants. Pediatrics 131, e1937–45.
| Breast milk-acquired cytomegalovirus infection and disease in VLBW and premature infants.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 23713111PubMed |
[34] Tengsupakul, S. et al. (2013) Asymptomatic DNAemia heralds CMV-associated NEC: case report, review, and rationale for preemption. Pediatrics 132, e1428–34.
| Asymptomatic DNAemia heralds CMV-associated NEC: case report, review, and rationale for preemption.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 24144715PubMed |
[35] Nigro, G. et al. (2010) Oral gancyclovir therapy for immunocompetent infants with cytomegalovirus-associated hemorrhagic or intractable enterocolitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 50, 111–113.
| Oral gancyclovir therapy for immunocompetent infants with cytomegalovirus-associated hemorrhagic or intractable enterocolitis.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD1MXhs1Wis73L&md5=e9d68a3fde4fd99751cdc905e18bab7aCAS | 19779376PubMed |
[36] Refai, Z. et al. (2012) Infant death due to CMV enterocolitis. BMJ Case Rep. , .
| Infant death due to CMV enterocolitis.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 22707698PubMed |
[37] Novakova, V. et al. (2014) Severe postnatal CMV colitis with an extensive colonic stenosis in a 2-month-old male immunocompetent term infant infected via breast milk. J. Clin. Virol. 59, 259–263.
| Severe postnatal CMV colitis with an extensive colonic stenosis in a 2-month-old male immunocompetent term infant infected via breast milk.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:STN:280:DC%2BC2cvmsVCgtA%3D%3D&md5=430d9d25012f2740f10748af8a990998CAS | 24553057PubMed |
[38] Hamprecht, K. et al. (2004) Cytomegalovirus (CMV) inactivation in breast milk: reassessment of pasteurization and freeze-thawing. Pediatr. Res. 56, 529–535.
| Cytomegalovirus (CMV) inactivation in breast milk: reassessment of pasteurization and freeze-thawing.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 15295084PubMed |
[39] Goelz, R. et al. (2009) Effects of different CMV-heat-inactivation-methods on growth factors in human breast milk. Pediatr. Res. 65, 458–461.
| Effects of different CMV-heat-inactivation-methods on growth factors in human breast milk.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD1MXjt1SntLw%3D&md5=452abe38b485ede4f2fa5f3e370c6f37CAS | 19127217PubMed |
[40] Maschmann, J. et al. (2006) Freeze-thawing of breast milk does not prevent cytomegalovirus transmission to a preterm infant. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 91, F288–F290.
| Freeze-thawing of breast milk does not prevent cytomegalovirus transmission to a preterm infant.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:STN:280:DC%2BD28znsVClsg%3D%3D&md5=8eff5e9804861df8b307ef262fbb1b50CAS | 16790732PubMed |
[41] Curtis, N. et al. (2005) Cytomegalovirus remains viable in naturally infected breast milk despite being frozen for 10 days. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 90, F529–F530.
| Cytomegalovirus remains viable in naturally infected breast milk despite being frozen for 10 days.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:STN:280:DC%2BD2MrpslCisA%3D%3D&md5=a4bd85127bb0a8b54e83ea8efc808f69CAS | 16244213PubMed |
[42] Paryani, S.G. et al. (1985) Sequelae of acquired cytomegalovirus infection in premature and sick term infants. J. Pediatr. 107, 451–456.
| Sequelae of acquired cytomegalovirus infection in premature and sick term infants.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 1:STN:280:DyaL2M3pt1ektQ%3D%3D&md5=65a5669bda0e20c0f9f153dee1c10292CAS | 2993576PubMed |
[43] Vollmer, B. et al. (2004) Postnatally acquired cytomegalovirus infection via breast milk: effects on hearing and development in preterm infants. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 23, 322–327.
| Postnatally acquired cytomegalovirus infection via breast milk: effects on hearing and development in preterm infants.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 15071286PubMed |
[44] Goelz, R. et al. (2013) Long-term cognitive and neurological outcome of preterm infants with postnatally acquired CMV infection through breast milk. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 98, F430–F433.
| Long-term cognitive and neurological outcome of preterm infants with postnatally acquired CMV infection through breast milk.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 23603882PubMed |
[45] Brecht, K.F. et al. (2015) Postnatal human cytomegalovirus infection in preterm infants has long-term neuropsychological sequelae. J. Pediatr. 166, 834–839.e1.
| Postnatal human cytomegalovirus infection in preterm infants has long-term neuropsychological sequelae.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25466679PubMed |
[46] Wright, C.J. and Permar, S.R. (2015) Preventing postnatal cytomegalovirus infection in the preterm infant: should it be done, can it be done, and at what cost? J. Pediatr. 166, 795–798.
| Preventing postnatal cytomegalovirus infection in the preterm infant: should it be done, can it be done, and at what cost?Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25662832PubMed |
Biographies
Klaus Hamprecht, MD, PhD, is a clinical virologist at the Institute of Medical Virology, University Hospital of Tuebingen, Germany. He completed his PhD and MD at Friedrich-Miescher Laboratory of the Max-Planck-Society in Tuebingen (1986, 1988). He is also an Adjunct Professor at the consiliary laboratory for congenital and postnatal CMV infection of the Robert-Koch-Institute, Berlin.
Rangmar Goelz, MD, is Senior Neonatologist and Vice Director of the Department of Neonatology, University Children’s Hospital Tuebingen. He studied Medicine at the Universities of Giessen and Heidelberg (1975–1982) and obtained his MD at the University of Tuebingen (1984).