Composite phosphorylated-modified rice straw prepared for highly effective immobilisation of cadmium in agriculture contaminated soil
Xiaohui Li A , Xianbin Ai B * , Xiyang Wang A , Liang Li A , Zaijun Xin A and Xiaoyan Sun A
B * , Xiyang Wang A , Liang Li A , Zaijun Xin A and Xiaoyan Sun A
A Jiangxi Engineering and Technology Research Center for Ecological Remediation of Heavy Metal Pollution, Institute of Microbiology, Jiangxi Academy of Science, Nanchang 330096, China.
B Institute of Energy Research, Jiangxi Academy of Science, Nanchang 330096, China.
Environmental Chemistry 19(8) 495-505 https://doi.org/10.1071/EN22041
Submitted: 9 May 2022 Accepted: 25 November 2022 Published: 15 February 2023
© 2022 The Author(s) (or their employer(s)). Published by CSIRO Publishing.
Environmental context. Rice straw is generated in vast quantities each year, but although the cellulose structure is stable, only 20% is used effectively. The structure of rice straw gives it high porosity and active functional groups, which means it easily adsorbs metals, but few studies have applied it to metal-contaminated soil. This study showed that composite phosphorylated-rice straw can be highly effective for the immobilization of cadmium in contaminated soils.
Rationale. Rice straw is generated in vast quantities each year, but the effective utilisation rate is low. In order to develop full utilisation of rice straw and seek high-efficiency immobilising agents for cadmium contaminated soil, the objectives of this paper was to prepare a new modified rice straw material.
Methodology. Composite phosphorylated rice straw (CPRS) and phosphorylated rice straw (PRS) were synthesised, the apparent morphology and functional groups of CPRS and PRS were characterised by SEM-EDS and FT-IR, and the remediation ability of CPRS and PRS on cadmium contaminated soil were studied by pot experiment.
Results. The results showed that the order of maximum adsorption capacity (Qmax) for Cd2+ was CPRS > PRS > RS, Qmax of CPRS for Cd2+ was 53.57 g kg−1. CPRS had a richer porosity, evidenced a 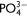 group stretching vibration and had calcium salt well-dispersed on its surface. The application of CPRS to Cd contaminated soil significantly improved the plant biomass (fresh biomass increased 66.97%, over control) and decreased the Chinese cabbage uptake of Cd (decreased 67.16%, over control). The chemical stability of cadmium in soil was enhanced by applying CPRS due to a decrease in the exchangeable Cd in soil in proportion (decreased 95.38–99.10%) to the increasing fractions of Cd bound to Fe/Mn oxides (increased 141.15–158.90%), and residual Cd (increased 4.76–6.99 times) following the application of CPRS as compared to control treatments.
group stretching vibration and had calcium salt well-dispersed on its surface. The application of CPRS to Cd contaminated soil significantly improved the plant biomass (fresh biomass increased 66.97%, over control) and decreased the Chinese cabbage uptake of Cd (decreased 67.16%, over control). The chemical stability of cadmium in soil was enhanced by applying CPRS due to a decrease in the exchangeable Cd in soil in proportion (decreased 95.38–99.10%) to the increasing fractions of Cd bound to Fe/Mn oxides (increased 141.15–158.90%), and residual Cd (increased 4.76–6.99 times) following the application of CPRS as compared to control treatments.
Discussion. CPRS had an excellent immobilisation ability for cadmium contaminated soil, which was related to improved soil pH and cation exchange capacity. It possibly immobilises Cd in the soil via surface complexation through Cd–O groups at the surface of CPRS. Modified rice straw materials could be highly recommended as an efficient stabiliser to immobilise Cd in polluted agricultural soils.
Keywords: cadmium, cadmium accumulation, Chinese cabbage, composite, immobilising agents, phosphorylated, rice straw, soil remediation.
References
Abah J, Mashebe P, Ubw ST, Denuga DD (2014). Some heavy metals content of Cabbage and soil cultivated in the Bezi Bar farm area of Katima Mulilo, Namibia. American Journal of Chemistry 4, 101–108.| Some heavy metals content of Cabbage and soil cultivated in the Bezi Bar farm area of Katima Mulilo, Namibia.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Anastopoulos I, Bhatnagar A, Hameed BH, Ok YS, Omirou M (2017). A review on waste-derived adsorbents from sugar industry for pollutant removal in water and wastewater. Journal of Molecular Liquids 240, 179–188.
| A review on waste-derived adsorbents from sugar industry for pollutant removal in water and wastewater.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Aparicio E, Rodríguez-Jasso RM, Pinales-Márquez CD, Loredo-Treviño A, Robledo-Olivo A, Aguilar CN, Kostas ET, Ruiz HA (2021). High-pressure technology for Sargassum spp biomass pretreatment and fractionation in the third generation of bioethanol production. Bioresource Technology 329, 124935
| High-pressure technology for Sargassum spp biomass pretreatment and fractionation in the third generation of bioethanol production.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Austruy A, Shahid M, Xiong T, Castrec M, Payre V, Niazi NK, Sabir M, Dumat C (2014). Mechanisms of metal-phosphates formation in the rhizosphere soils of pea and tomato: Environmental and sanitary consequences. Journal of Soils and Sediments 14, 666–678.
| Mechanisms of metal-phosphates formation in the rhizosphere soils of pea and tomato: Environmental and sanitary consequences.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Bolan N, Kunhikrishnan A, Thangarajan R, Kumpiene J, Park J, Makino T, Kirkham MB, Scheckel K (2014). Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils – To mobilize or to immobilize?. Journal of Hazardous Materials 266, 141–166.
| Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils – To mobilize or to immobilize?.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Chen Q, Zheng JW, Wen LY, Yang C, Zhang LJ (2019). A multi-functional-group modified cellulose for enhanced heavy metal cadmium adsorption: Performance and quantum chemical mechanism. Chemosphere 224, 509–518.
| A multi-functional-group modified cellulose for enhanced heavy metal cadmium adsorption: Performance and quantum chemical mechanism.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Chen XN, Wang XH, Fang D (2020). A review on C1s XPS-spectra for some kinds of carbon materials. Fullerenes, Nanotubes and Carbon Nanostructures 28, 1048–1058.
| A review on C1s XPS-spectra for some kinds of carbon materials.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
El-Sayed GO, Dessouki HA, Ibrahiem SS (2011). Removal of Zn(II), Cd(II) and Mn(II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on maize stalks. The Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences 15, 8–21. Available at http://mjas.analis.com.my/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/El-Sayed.pdf
Fang W, Zhang H, Yin J, Yang B, Zhang Y, Li J, Yao F (2016). Hydroxyapatite crystal formation in the presence of polysaccharide. Crystal Growth & Design 16, 1247–1255.
| Hydroxyapatite crystal formation in the presence of polysaccharide.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Garba ZN, Ugbaga NI, Abdullahi AK (2016). Evaluation of optimum adsorption conditions for Ni (II) and Cd (II) removal from aqueous solution by modified plantain peels (MPP). Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5, 170–179.
| Evaluation of optimum adsorption conditions for Ni (II) and Cd (II) removal from aqueous solution by modified plantain peels (MPP).Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Garbo C, Sindilaru M, Carlea A, Tomoaia G, Almasan V, Petean I, Mocanu A, Horovitz O, Tomoaia-Cotisel M (2017). Synthesis and structural characterization of novel porous zinc substituted nanohydroxyapatite powders. Particulate Science and Technology 35, 29–37.
| Synthesis and structural characterization of novel porous zinc substituted nanohydroxyapatite powders.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Garg U, Kaur MP, Jawa GK, Sud D, Garg VK (2008). Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on agricultural waste biomass. Journal of Hazardous Materials 154, 1149–1157.
| Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on agricultural waste biomass.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Goodman BA (2020). Utilization of waste straw and husks from rice production: A review. Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts 5, 143–162.
| Utilization of waste straw and husks from rice production: A review.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Harja M, Buema G, Bulgariu L, Bulgariu D, Sutiman DM, Ciobanu G (2015). Removal of cadmium(II) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto modified algae and ash. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering 32, 1804–1811.
| Removal of cadmium(II) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto modified algae and ash.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Igalavithana AD, Lee SE, Lee YH, Tsang DCW, Rinklebe J, Kwon EE, Ok YS (2017). Heavy metal immobilization and microbial community abundance by vegetable waste and pine cone biochar of agricultural soils. Chemosphere 174, 593–603.
| Heavy metal immobilization and microbial community abundance by vegetable waste and pine cone biochar of agricultural soils.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Kathirselvam M, Kumaravel A, Arthanarieswaran VP, Saravanakumar SS (2019). Characterization of cellulose fibers in Thespesia populnea barks: Influence of alkali treatment. Carbohydrate Polymers 217, 178–189.
| Characterization of cellulose fibers in Thespesia populnea barks: Influence of alkali treatment.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Khalid S, Shahid M, Niazi NK, Murtaza B, Bibi I, Dumat C (2017). A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Journal of Geochemical Exploration 182, 247–268.
| A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Ko J-H, Kim W-C, Im JH, Kim J-Y, Patterson S, Han K-H (2018). Pathway-specific genetic pretreatment strategy to improve bioenergy feedstock. Biomass and Bioenergy 115, 253–259.
| Pathway-specific genetic pretreatment strategy to improve bioenergy feedstock.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Kumari D, Pan X, Lee DJ, Achal V (2014). Immobilization of cadmium in soil by microbially induced carbonate precipitation with Exiguobacterium undae at low temperature. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 94, 98–102.
| Immobilization of cadmium in soil by microbially induced carbonate precipitation with Exiguobacterium undae at low temperature.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Li YF, Wang LA, Zhang ZE, Hu XY, Cheng Y, Zhong C (2018). Carbon dioxide absorption from biogas by amino acid salt promoted potassium carbonate solutions in a hollow fiber membrane contactor: A numerical study. Energy & Fuels 32, 3637–3646.
| Carbon dioxide absorption from biogas by amino acid salt promoted potassium carbonate solutions in a hollow fiber membrane contactor: A numerical study.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983). Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochemical Society Transactions 11, 591–592.
| Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Łojewska J, Miśkowiec P, Łojewski T, Proniewicz LM (2005). Cellulose oxidative and hydrolytic degradation: In situ FTIR approach. Polymer Degradation and Stability 88, 512–520.
| Cellulose oxidative and hydrolytic degradation: In situ FTIR approach.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Lu RK (2000) ‘Soil agro-chemistrical analysis’. pp. 25–38. (China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing)
Ma JZ, Xia MZ, Zhu SD, Wang FY (2020). A new alendronate doped HAP nanomaterial for Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+ effect absorption. Journal of Hazardous Materials 400, 123143
| A new alendronate doped HAP nanomaterial for Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+ effect absorption.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Marchat D, Bernache-Assollant D, Champion E (2007). Cadmium fixation by synthetic hydroxyapatite in aqueous solution—Thermal behaviour. Journal of Hazardous Materials 139, 453–460.
| Cadmium fixation by synthetic hydroxyapatite in aqueous solution—Thermal behaviour.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Mo JH, Yang Q, Zhang N, Zhang WX, Zheng Y, Zhang ZE (2018). A review on agro-industrial waste (AIW) derived adsorbents for water and wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Management 227, 395–405.
| A review on agro-industrial waste (AIW) derived adsorbents for water and wastewater treatment.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Omo-Okoro PN, Daso AP, Okonkwo JO (2018). A review of the application of agricultural wastes as precursor materials for the adsorption of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: A focus on current approaches and methodologies. Environmental Technology & Innovation 9, 100–114.
| A review of the application of agricultural wastes as precursor materials for the adsorption of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: A focus on current approaches and methodologies.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Palansooriya KN, Shaheen SM, Chen SS, Tsang DCW, Hashimoto Y, Hou D, Bolan NS, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2020). Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: A critical review. Environment International 134, 105046
| Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: A critical review.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Qu JH, Meng XL, You H, Ye XQ, Du ZL (2017). Utilization of rice husks functionalized with xanthates as cost-effective biosorbents for optimal Cd(II) removal from aqueous solution via response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology 241, 1036–1042.
| Utilization of rice husks functionalized with xanthates as cost-effective biosorbents for optimal Cd(II) removal from aqueous solution via response surface methodology.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Ruiz HA, Conrad M, Sun SN, Sanchez A, Rocha GJM, Romaní A, Castro E, Torres A, Rodríguez-Jasso RM, Andrade LP, Smirnova I, Sun RC, Meyer AS (2020). Engineering aspects of hydrothermal pretreatment: From batch to continuous operation, scale-up and pilot reactor under biorefinery concept. Bioresource Technology 299, 122685
| Engineering aspects of hydrothermal pretreatment: From batch to continuous operation, scale-up and pilot reactor under biorefinery concept.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Saxena A, Bhardwaj M, Allen T, Kumar S, Sahney R (2017). Adsorption of heavy metals from wastewater using agricultural-industrial wastes as biosorbents. Water Science 31, 189–197.
| Adsorption of heavy metals from wastewater using agricultural-industrial wastes as biosorbents.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Shaheen SM, Shams MS, Khalifa MR, El-Dali MA, Rinklebe J (2017). Various soil amendments and environmental wastes affect the (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of potentially toxic elements in a sewage effluent irrigated sandy soil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 142, 375–387.
| Various soil amendments and environmental wastes affect the (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of potentially toxic elements in a sewage effluent irrigated sandy soil.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Shahid M, Sabir M, Ali MA, Ghafoor A (2014). Effect of organic amendments on phytoavailability of nickel and growth of berseem (Trifolium alexandrinum) under nickel contaminated soil conditions. Chemical Speciation & Bioavailability 26, 37–42.
| Effect of organic amendments on phytoavailability of nickel and growth of berseem (Trifolium alexandrinum) under nickel contaminated soil conditions.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Shahril SM, Ridzuan MJM, Abdul Majid MS, Bariah AMN, Rahman MTA, Narayanasamy P (2022). Alkali treatment influence on cellulosic fiber from Furcraea foetida leaves as potential reinforcement of polymeric composites. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 19, 2567–2583.
| Alkali treatment influence on cellulosic fiber from Furcraea foetida leaves as potential reinforcement of polymeric composites.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Shen JB, Yuan LX, Zhang JL, Li HG, Bai ZH, Chen XP, Zhang WF, Zhang FS (2011). Phosphorus dynamics: From soil to plant. Plant Physiology 156, 997–1005.
| Phosphorus dynamics: From soil to plant.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Singh SR, Singh AP (2017). Adsorption of heavy metals from waste waters using waste biomass. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology 6, 423–428.
| Adsorption of heavy metals from waste waters using waste biomass.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Sukmawan R, Kusmono , Rahmanta AP, Saputri LH (2022). The effect of repeated alkali pretreatments on the morphological characteristics of cellulose from oil palm empty fruit bunch fiber-reinforced epoxy adhesive composite. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives 114, 103095
| The effect of repeated alkali pretreatments on the morphological characteristics of cellulose from oil palm empty fruit bunch fiber-reinforced epoxy adhesive composite.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Sun L, Wu Q, Liao K, Yu P, Cui Q, Rui Q, Wang D (2016). Contribution of heavy metals to toxicity of coal combustion related fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in Caenorhabditis elegans with wild-type or susceptible genetic background. Chemosphere 144, 2392–2400.
| Contribution of heavy metals to toxicity of coal combustion related fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in Caenorhabditis elegans with wild-type or susceptible genetic background.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Sun MX, Xu XB, Wang CD, Bai YL, Fu C, Zhang LX, Fu R, Wang YT (2020). Environmental burdens of the comprehensive utilization of straw: Wheat straw utilization from a life-cycle perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production 259, 120702
| Environmental burdens of the comprehensive utilization of straw: Wheat straw utilization from a life-cycle perspective.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry 51, 844–851.
| Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Wang M, Wu S, Guo J, Zhang X, Yang Y, Chen F, Zhu R (2019). Immobilization of cadmium by hydroxyapatite converted from microbial precipitated calcite. Journal of Hazardous Materials 366, 684–693.
| Immobilization of cadmium by hydroxyapatite converted from microbial precipitated calcite.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Wang WS, Yang SQ, Zhang AP, Yang ZL (2021). Synthesis of a slow-release fertilizer composite derived from waste straw that improves water retention and agricultural yield. Science of the Total Environment 768, 144978
| Synthesis of a slow-release fertilizer composite derived from waste straw that improves water retention and agricultural yield.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Wollbrink A, Rüscher CH, Volgmann K, Koch J, Breuksch A, Tegenkamp C, Caro J (2017). Improved hydrogen selectivity of surface modified graphite (SMG) membranes: Permeation experiments and characterisation by microRaman Spectroscopy and XPS. Journal of Membrane Science 528, 316–325.
| Improved hydrogen selectivity of surface modified graphite (SMG) membranes: Permeation experiments and characterisation by microRaman Spectroscopy and XPS.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Yan Y, Zhang Z, Zhang L, Chen Y, Tang Q (2014). Dynamic modeling of biogas upgrading in hollow fiber membrane contactors. Energy & Fuels 28, 5745–5755.
| Dynamic modeling of biogas upgrading in hollow fiber membrane contactors.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Yin GC, Song XW, Tao L, Sarkar B, Sarmah AK, Zhang WX, Lin QT, Xiao RB, Liu QJ, Wang HL (2020). Novel Fe-Mn binary oxide-biochar as an adsorbent for removing Cd(II) from aqueous solutions. Chemical Engineering Journal 389, 124465
| Novel Fe-Mn binary oxide-biochar as an adsorbent for removing Cd(II) from aqueous solutions.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Zhang XX, Ma F (2015). Emergy evaluation of different straw reuse technologies in northeast China. Sustainability 7, 11360–11377.
| Emergy evaluation of different straw reuse technologies in northeast China.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Zheng LC, Meng PP (2016). Preparation, characterization of corn stalk xanthates and its feasibility for Cd (II) removal from aqueous solution. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers 58, 391–400.
| Preparation, characterization of corn stalk xanthates and its feasibility for Cd (II) removal from aqueous solution.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Zhou XL, Xu ZQ, He J, Li YQ, Pan CX, Wang CL, Deng M-R, Zhu HH (2020). A myxobacterial LPMO10 has oxidizing cellulose activity for promoting biomass enzymatic saccharification of agricultural crop straws. Bioresource Technology 318, 124217
| A myxobacterial LPMO10 has oxidizing cellulose activity for promoting biomass enzymatic saccharification of agricultural crop straws.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Zhu YN, Zhu ZQ, Zhao X, Liang YP, Dai LQ, Huang YH (2016). Characterization, dissolution and solubility of cadmium–calcium hydroxyapatite solid solutions at 25 °C. Chemical Geology 423, 34–48.
| Characterization, dissolution and solubility of cadmium–calcium hydroxyapatite solid solutions at 25 °C.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |


