Reproduction, Fertility and Development
Volume 32
Number 14 2020
Obesity is an important cause of female infertility. The altered endocrine and lipid profile in obese conditions can create a poor ovarian microenvironment and decrease the functional competence of oocytes because of an increases in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Future research directed towards mitigating ER stress in oocytes may help to improve reproductive outcomes in this group of patients.
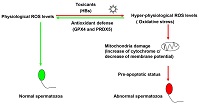
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) may have adverse effects on human spermatozoa and reduce fertilisation capacity. In this study we investigated how human spermatozoa responded to HBV surface protein (HBs). Treatment of spermatozoa with HBs induced reactive oxygen species (ROS), as well as antioxidant defences of glutathione peroxidase 4 and peroxiredoxin 5 to counter the increased levels of ROS. The findings provide new evidence regarding the molecular mechanism involved in HBs-induced oxidative stress in spermatozoa.
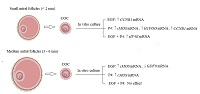
Oocyte growth and maturation are coordinated by different factors that may be involved in the storage of mRNA. However, it is not known whether epidermal growth factor (EGF) and progesterone (P4), alone or in combination, increase levels of mRNAs in cumulus–oocyte complexes cultured in vitro. This study shows that P4 increases oocyte maturation factor Mos (cMOS), oocyte-specific histone H1 (H1FOO) and cyclin B1 (CCNB1) mRNA levels after the culture of oocytes from small antral follicles, whereas in oocytes from medium-sized antral follicles EGF and P4 increase cMOS mRNA levels.
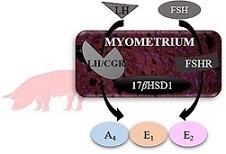
In pigs, the production of uterine steroid hormones contributes to the regulation of the oestrous cycle and pregnancy. Regulation of steroid hormone production, especially by the muscular layer of the uterus, is not well characterised. This study tested the effects of pituitary-derived hormones (LH and FSH) on the release of steroid hormones from the muscular layer of the uterus. The results of this study will help us understand the regulation of the steroidogenic activity in the myometrium.
Artificial reproduction is an important way to protect Onychostoma macrolepis, an atypical cave fish in China. In this study, the addition of 1 μM melatonin to semen increased the fertilising capacity of spermatozoa by decreasing ROS accumulation in spermatozoa during semen preservation in vitro. This study establishes an efficient method for sperm preservation in vitro, which can be used to breed O. macrolepis.
The detection of signals from cells surrounding the mammalian egg during fertilisation could provide a diagnostic means of determining future development potential in vitro. This study examined whether the release of calcium from these surrounding cells reflected developmental potential. Although the experimental conditions caused a release of calcium in the presence or absence of spermatozoa, the pattern of loss with spermatozoa differs considerably, posing important questions about the role of these egg-supporting cells during fertilisation.
 and Guruprasad Kalthur
and Guruprasad Kalthur