Insulin-like growth factors 1 and 2 are associated with testicular germ cell proliferation and apoptosis during fish reproduction
Davidson P. Moreira A , Rafael M. C. Melo A , André A. Weber A and Elizete Rizzo A B
A B
A Departamento de Morfologia, Instituto de Ciências Biológicas, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, CP 486, 31270-901 Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil.
B Corresponding author. Email: ictio@icb.ufmg.br
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 32(11) 988-998 https://doi.org/10.1071/RD20128
Submitted: 15 May 2020 Accepted: 2 June 2020 Published: 1 July 2020
Abstract
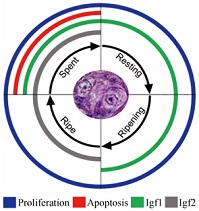
To support sperm production, fish testes undergo intense tissue remodelling, with endocrine, paracrine and autocrine signals regulating gonad physiology. The aim of this study was to investigate the testicular expression of insulin-like growth factor (Igf) 1 and Igf2 during spermatogenesis, and their relationship with cell proliferation and apoptosis throughout the reproductive cycle. The study was performed in male Hypostomus garmani, a catfish living in headwater rivers of the São Francisco River basin, Brazil. Spermatogenesis was analysed using histology, morphometry, immunohistochemistry and terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP–digoxigenin nick end-labelling (TUNEL) analysis at different maturity stages. The results showed the proliferation of spermatogonia throughout the reproductive cycle, with a higher rate during the ripe stage. Germ and Sertoli cells expressed Igf1 at all stages of testicular maturity, Igf2 was predominant at the ripe stage and both Igf1 and Igf2 occurred at the spent stage. Caspase-3 and TUNEL analysis revealed a higher rate of apoptosis at the spent stage associated with reduced expression of Igf1 and Igf2. Sertoli cell proliferation was associated with spermatogonia and spermatocyte cysts at different stages of the reproductive cycle. Together, the data support a proliferative role for Igf1 and Igf2 in regulating testicular apoptosis in H. garmani, with cyclical variation in their expression during gonad maturation.
Additional keywords: caspase-3, Hypostomus garmani, Ki-67, spermatogenesis, terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP–digoxigenin nick end-labelling (TUNEL).
References
Baumgarten, S. C., Convissar, S. M., Zamah, A. M., Fierro, M. A., Winston, N. J., Scoccia, B., and Stocco, C. (2015). FSH regulates IGF-2 expression in human granulosa cells in an AKT-dependent manner. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100, E1046–E1055.| FSH regulates IGF-2 expression in human granulosa cells in an AKT-dependent manner.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 26066673PubMed |
Berishvili, G., D’Cotta, H., Baroiller, J. F., Segner, H., and Reinecke, M. (2006). Differential expression of IGF-I mRNA and peptide in the male and female gonad during early development of a bony fish, the tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 146, 204–210.
| Differential expression of IGF-I mRNA and peptide in the male and female gonad during early development of a bony fish, the tilapia Oreochromis niloticus.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 16412440PubMed |
Caelers, A., Berishvili, G., Meli, M. L., Eppler, E., and Reinecke, M. (2004). Establishment of a real-time RT-PCR for the determination of absolute amounts of IGF-I and IGF-II gene expression in liver and extrahepatic sites of the tilapia. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 137, 196–204.
| Establishment of a real-time RT-PCR for the determination of absolute amounts of IGF-I and IGF-II gene expression in liver and extrahepatic sites of the tilapia.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 15158131PubMed |
Casatti, L., and Castro, R. M. C. (1998). A fish community of the São Francisco River headwaters riffles, southeastern Brazil. Ichthyol. Explor. Freshwat. 9, 229–242.
Chandrashekar, V., Zaczek, D., and Bartke, A. (2004). The consequences of altered somatotropic system on reproduction. Biol. Reprod. 71, 17–27.
| The consequences of altered somatotropic system on reproduction.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 15028633PubMed |
Chaves-Pozo, E., Mulero, V., Meseguer, J., and García Ayala, A. (2005). An overview of cell renewal in the testis throughout the reproductive cycle of a seasonal breeding teleost, the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L). Biol. Reprod. 72, 593–601.
| An overview of cell renewal in the testis throughout the reproductive cycle of a seasonal breeding teleost, the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L).Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 15548730PubMed |
Corriero, A., Desantis, S., Bridges, C. R., Kime, D. E., Megalofonou, P., Santamaria, N., Cirillo, F., Ventriglia, G., Di Summa, A., Deflorio, M., Campobasso, F., and De Metrio, G. (2007). Germ cell proliferation and apoptosis during different phases of swordfish (Xiphias gladius L.) spermatogenetic cycle. J. Fish Biol. 70, 83–99.
| Germ cell proliferation and apoptosis during different phases of swordfish (Xiphias gladius L.) spermatogenetic cycle.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Cuylen, S., Blaukopf, C., Politi, A. Z., Muller-Reichert, T., Neumann, B., Poser, I., Ellenberg, J., Hyman, A. A., and Gerlich, D. W. (2016). Ki-67 acts as a biological surfactant to disperse mitotic chromosomes. Nature 535, 308–312.
| Ki-67 acts as a biological surfactant to disperse mitotic chromosomes.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 27362226PubMed |
De Rooij, D. G. (2006). Regulation of spermatogonial stem cell behavior in vivo and in vitro. Anim. Reprod. 3, 130–134.
Domingos, F. F. T., Thomé, R. G., Martinelli, P. M., Sato, Y., Bazzoli, N., and Rizzo, E. (2013). Role of HSP70 in the regulation of the testicular apoptosis in a seasonal breeding teleost Prochilodus argenteus from the São Francisco river, Brazil. Microsc. Res. Tech. 76, 350–356.
| Role of HSP70 in the regulation of the testicular apoptosis in a seasonal breeding teleost Prochilodus argenteus from the São Francisco river, Brazil.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Duan, C. (1997). The insulin-like growth factor system and its biological actions in fish. Am. Zool. 37, 491–503.
| The insulin-like growth factor system and its biological actions in fish.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
França, L. R., Nóbrega, R. H., Morais, R., Assis, L. H. D. C., and Schultz, R. (2015). Sertoli cell structure and function in anamniote vertebrates. In ‘Sertoli Cell Biology’. (Ed. MDBT Griswold.) pp. 385–407. (Academic Press: Oxford.)
Garavello, J. C., and Garavello, J. P. (2004). Spatial distribution and interaction of four species of the catfish genus Hypostomus Lacépède with bottom of Rio São Francisco, Canindé do São Francisco, Sergipe, Brazil (Pisces, Loricariidae, Hypostominae). Braz. J. Biol. 64, 591–598.
| Spatial distribution and interaction of four species of the catfish genus Hypostomus Lacépède with bottom of Rio São Francisco, Canindé do São Francisco, Sergipe, Brazil (Pisces, Loricariidae, Hypostominae).Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 15619997PubMed |
Griffeth, R. J., Bianda, V., and Nef, S. (2014). The emerging role of insulin-like growth factors in testis development and function. Basic Clin. Androl. 24, 12.
| The emerging role of insulin-like growth factors in testis development and function.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25780585PubMed |
Ipsa, E., Cruzat, V. F., Kagize, J. N., Yovich, J. L., and Keane, K. N. (2019). Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor action in reproductive tissues. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 10, 777.
| Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor action in reproductive tissues.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 31781044PubMed |
Le Gac, F., Loir, M., Le Bail, P. Y., and Ollitrault, M. (1996). Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) mRNA and IGF-I receptor in trout testis and in isolated spermatogenic and Sertoli cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 44, 23–35.
| Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) mRNA and IGF-I receptor in trout testis and in isolated spermatogenic and Sertoli cells.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 8722689PubMed |
Lei, Q., Chen, S., and Hua, J. (2019). H19 regulates the proliferation of bovine male germline stem cells via IGF-1 signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 915–926.
| H19 regulates the proliferation of bovine male germline stem cells via IGF-1 signaling pathway.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Li, J., Chu, L., Sun, X., Liu, Y., and Cheng, C. H. K. (2015). IGFs mediate the action of LH on oocyte maturation in zebrafish. Mol. Endocrinol. 29, 373–383.
| IGFs mediate the action of LH on oocyte maturation in zebrafish.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25584412PubMed |
Lujan, N. K., Armbruster, J. W., Lovejoy, N. R., and López-fernández, H. (2015). Multilocus molecular phylogeny of the suckermouth armored catfishes (Siluriformes: Loricariidae) with a focus on subfamily Hypostominae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 82, 269–288.
| Multilocus molecular phylogeny of the suckermouth armored catfishes (Siluriformes: Loricariidae) with a focus on subfamily Hypostominae.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25193609PubMed |
Maldonado, C., Cea, P., Adasme, T., Collao, A., Díaz-Araya, G., Chiong, M., and Lavandero, S. (2005). IGF-1 protects cardiac myocytes from hyperosmotic stress-induced apoptosis via CREB. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336, 1112–1118.
| IGF-1 protects cardiac myocytes from hyperosmotic stress-induced apoptosis via CREB.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 16168389PubMed |
McClusky, L. M. (2013). The caspase-dependent apoptosis gradient in the testis of the blue shark, Prionace glauca. Reproduction 145, 297–310.
| The caspase-dependent apoptosis gradient in the testis of the blue shark, Prionace glauca.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 23580951PubMed |
Melo, R. M. C., Ribeiro, Y. M., Luz, R. K., and Bazzoli, N. (2016). Influence of low temperature on structure and dynamics of spermatogenesis during culture of Oreochromis niloticus. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 172, 148–156.
| Influence of low temperature on structure and dynamics of spermatogenesis during culture of Oreochromis niloticus.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Miura, T., Yamauchi, K., Takahashi, H., and Nagahama, Y. (1991). Hormonal induction of all stages of spermatogenesis in vitro in the male Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 5774–5778.
| Hormonal induction of all stages of spermatogenesis in vitro in the male Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica).Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 2062857PubMed |
Moreira, D. P., Pinheiro, A. P. B., Melo, R. M. C., Weber, A. A., Bazzoli, N., and Rizzo, E. (2017). Gametogênese e estratégias reprodutivas de quatro espéccies de peixes do Alto Rio das Velhas, Minas Gerais. In ‘Anais do XXII Encontro Brasileiro de Ictiologia, Porto Seguro, Brazil, 2017.’ p. 278. (Sociedade Brasileira de Ictiologia)
Nakayama, Y., Yamamoto, T., and Abé, S. I. (1999). IGF-I, IGF-II and insulin promote differentiation of spermatogonia to primary spermatocytes in organ culture of newt testes. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 43, 343–347.
| 10470651PubMed |
Neto, F. T. L., Bach, P. V., Najari, B. B., Li, P. S., and Goldstein, M. (2016). Spermatogenesis in humans and its affecting factors. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 59, 10–26.
| Spermatogenesis in humans and its affecting factors.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Nóbrega, R. H., De Souza Morais, R. D. V., Crespo, D., De Waal, P. P., De França, L. R., Schulz, R. W., and Bogerd, J. (2015). Fsh stimulates spermatogonial proliferation and differentiation in zebrafish via Igf3. Endocrinology 156, 3804–3817.
| Fsh stimulates spermatogonial proliferation and differentiation in zebrafish via Igf3.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 26207345PubMed |
Perrot, V., and Funkenstein, B. (1999). Cellular distribution of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) mRNA and hormonal regulation of IGF-I and IGF-II mRNA expression in rainbow trout testis (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 20, 219–229.
| Cellular distribution of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) mRNA and hormonal regulation of IGF-I and IGF-II mRNA expression in rainbow trout testis (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Pitetti, J.-L., Calvel, P., Zimmermann, C., Conne, B., Papaioannou, M. D., Aubry, F., Cederroth, C. R., Urner, F., Fumel, B., Crausaz, M., Docquier, M., Herrera, P. L., Pralong, F., Germond, M., Guillou, F., Jégou, B., and Nef, S. (2013). An essential role for insulin and IGF1 receptors in regulating Sertoli cell proliferation, testis size, and FSH action in mice. Mol. Endocrinol. 27, 814–827.
| An essential role for insulin and IGF1 receptors in regulating Sertoli cell proliferation, testis size, and FSH action in mice.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 23518924PubMed |
Prado, P. S., Paula, A., Pinheiro, B., Weber, A. A., Bazzoli, N., and Rizzo, E. (2019). Expression patterns and immunolocalisation of IGF-I and IGF-II in male and female gonads of the Neotropical characid fish Astyanax fasciatus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 45, 167–176.
| Expression patterns and immunolocalisation of IGF-I and IGF-II in male and female gonads of the Neotropical characid fish Astyanax fasciatus.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 30143929PubMed |
Regan, C. T. (1904). ‘A Monograph of the Fishes of the Family Loricariidae.’ (Transactions of the Zoological Society of London: London.)
Reindl, K. M., and Sheridan, M. A. (2012). Peripheral regulation of the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor system in fish and other vertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 163, 231–245.
| Peripheral regulation of the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor system in fish and other vertebrates.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 22909791PubMed |
Reinecke, M. (2010a). Insulin-like growth factors and fish reproduction. Biol. Reprod. 82, 656–661.
| Insulin-like growth factors and fish reproduction.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19864315PubMed |
Reinecke, M. (2010b). Influences of the environment on the endocrine and paracrine fish growth hormone–insulin-like growth factor-I system. J. Fish Biol. 76, 1233–1254.
| Influences of the environment on the endocrine and paracrine fish growth hormone–insulin-like growth factor-I system.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 20537012PubMed |
Ribeiro, Y. M., de Matos, S. A., Domingos, F. F. T., dos Santos, H. B., Cruz Vieira, A. B., Bazzoli, N., and Rizzo, E. (2017). Germ cell proliferation and apoptosis during testicular regression in a seasonal breeding fish kept in captivity. Tissue Cell 49, 664–671.
| Germ cell proliferation and apoptosis during testicular regression in a seasonal breeding fish kept in captivity.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 28919010PubMed |
Rizzo, E., and Bazzoli, N. (2020). Reproduction and embryogenesis. ‘Biology and Physiology of Freshwater Neotropical Fish’. (Eds B. Baldisserotto, E. C. Urbinati, and J. Cyrino.) pp. 287–313. (Academic Press, Elsevier: London.)
Sales, C. F., Lemos, F. S., Morais, R. D. V. S., Thome, R. G., Santos, H. B., Pinheiro, A. P. B., Bazzoli, N., and Rizzo, E. (2019). Thermal stress induces heat shock protein 70 and apoptosis during embryo development in a Neotropical freshwater fish. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 31, 547–556.
| Thermal stress induces heat shock protein 70 and apoptosis during embryo development in a Neotropical freshwater fish.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 30373705PubMed |
Schlatt, S., and Ehmcke, J. (2014). Regulation of spermatogenesis: an evolutionary biologist’s perspective. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 29, 2–16.
| Regulation of spermatogenesis: an evolutionary biologist’s perspective.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 24685618PubMed |
Scholzen, T., and Gerdes, J. (2000). The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J. Cell. Physiol. 182, 311–322.
| The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 10653597PubMed |
Schulz, R. W., and Miura, T. (2002). Spermatogenesis and its endocrine regulation. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 26, 43–56.
| Spermatogenesis and its endocrine regulation.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Schulz, R. W., Menting, S., Bogerd, J., França, L. R., Vilela, D. A. R., and Godinho, H. P. (2005). Sertoli cell proliferation in the adult testis – evidence from two fish species belonging to different orders. Biol. Reprod. 73, 891–898.
| Sertoli cell proliferation in the adult testis – evidence from two fish species belonging to different orders.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 16000552PubMed |
Schulz, R. W., de França, L. R., Lareyre, J. J., LeGac, F., Chiarini-Garcia, H., Nobrega, R. H., and Miura, T. (2010). Spermatogenesis in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 165, 390–411.
| Spermatogenesis in fish.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19348807PubMed |
Shelton, J. G., Steelman, L. S., White, E. R., and McCubrey, J. A. (2004). Synergy between PI3K/Akt and Raf/MEK/ERK pathways in IGF-1R mediated cell cycle progression and prevention of apoptosis in hematopoietic cells. Cell Cycle 3, 370–377.
| Synergy between PI3K/Akt and Raf/MEK/ERK pathways in IGF-1R mediated cell cycle progression and prevention of apoptosis in hematopoietic cells.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Shukla, K. K., Mahdi, A. A., and Rajender, S. (2012). Apoptosis, spermatogenesis and male infertility. Front. Biosci. E4, 746–754.
| Apoptosis, spermatogenesis and male infertility.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Tang, D., Huang, Y., Liu, W., and Zhang, X. (2016). Up-regulation of microRNA-210 is associated with spermatogenesis by targeting IGF2 in male infertility. Med. Sci. Monit. 22, 2905–2910.
| Up-regulation of microRNA-210 is associated with spermatogenesis by targeting IGF2 in male infertility.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 27535712PubMed |
Tse, M. C. L., Vong, Q. P., Cheng, C. H. K., and Chan, K. M. (2002). PCR-cloning and gene expression studies in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) insulin-like growth factor-II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1575, 63–74.
| PCR-cloning and gene expression studies in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) insulin-like growth factor-II.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Viñas, J., and Piferrer, F. (2008). Stage-specific gene expression during fish spermatogenesis as determined by laser-capture microdissection and quantitative-PCR in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) gonads. Biol. Reprod. 79, 738–747.
| Stage-specific gene expression during fish spermatogenesis as determined by laser-capture microdissection and quantitative-PCR in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) gonads.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 18614701PubMed |
Yao, J., Zuo, H., Gao, J., Wang, M., Wang, D., and Li, X. (2017). The effects of IGF-1 on mouse spermatogenesis using an organ culture method. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 491, 840–847.
| The effects of IGF-1 on mouse spermatogenesis using an organ culture method.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 28552527PubMed |
Yin, Y., Stahl, B. C., DeWolf, W. C., and Morgentaler, A. (1998). P53-mediated germ cell quality control in spermatogenesis. Dev. Biol. 204, 165–171.
| P53-mediated germ cell quality control in spermatogenesis.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 9851850PubMed |
Zawadzki, C. H., Birindelli, J. L. O., and Lima, F. C. T. (2008). A new pale-spotted species of Hypostomus Lacépède (Siluriformes: Loricariidae) from the Rio Tocantins and Rio Xingu basins in central Brazil. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 6, 395–402.
| A new pale-spotted species of Hypostomus Lacépède (Siluriformes: Loricariidae) from the Rio Tocantins and Rio Xingu basins in central Brazil.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |


