210 INCREASE IN OVULATION RATE AFTER IMMUNIZATION OF MALPURA EWES AGAINST A SYNTHETIC PEPTIDE SEQUENCE OF THE α-SUBUNIT OF BOVINE INHIBIN
S.M.K. Naqvi A , P. Palta B , A. Joshi A , R. Gulyani A , V. Paul B , V.P. Maurya A and R.S. Manik BA Central Sheep and Wool Research Institute, Mannavanur, Kodiakonal, India;;
B National Dairy Research Institute, Daemed University, Karnal, India. email: prabhatpalta@yahoo.com
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 16(2) 226-227 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv16n1Ab210
Submitted: 1 August 2003 Accepted: 1 October 2003 Published: 2 January 2004
Abstract
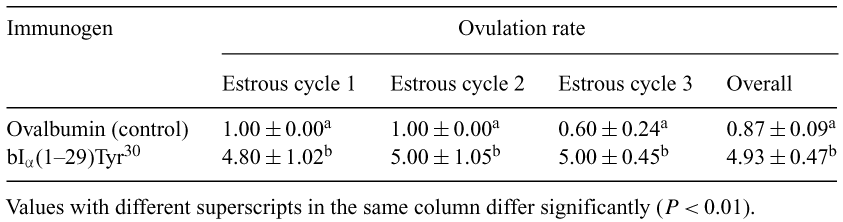
Unlike many other breeds of sheep (e.g. Boroola, Romney or Merino) which have high fecundity, the Malpura ewe, an Indian breed of sheep, is marked by an ovulation rate of one and a low incidence of twinning. Active immunization against a number of inhibin-based synthetic peptides has been reported to increase ovulation rates in these high fecundity breeds of sheep. The objective of the present study was to explore the possibility of increasing ovulation rates in Malpura ewes by active immunization against a synthetic peptide replica of the N-terminal sequence of the bovine inhibin. Adult Malpura ewes (n = 5) were actively immunized against a synthetic peptide that corresponded to the N-terminus of the α-subunit of bovine inhibin [bIα(1–29)Tyr30]. The peptide was conjugated to ovalbumin, with a peptide-to-ovalbumin ratio of around 20 moles mole−1, to increase its antigenicity. Control ewes (n = 5) were immunized against ovalbumin. On the day of primary immunization, 400 μg of peptide-ovalbumin conjugate or ovalbumin were dissolved in 1 mL of isotonic saline, emulsified with an equal volume of Freund’s complete adjuvant and injected at four sites in each ewe. Following this, boosters 1, 2 and 3 were given on Days 28, 56 and 84, respectively, of the experiment (Day 0 = day of primary immunization); boosters were 200 μg of peptide-ovalbumin conjugate or ovalbumin dissolved in 1 mL of isotonic saline and emulsified with an equal volume of Freund’s incomplete adjuvant. Estrus was synchronized by a double injection schedule of PGF2α (7.5 mg Lutalyse, once each on Days 35 and 45). The animals were subsequently allowed to undergo normal cyclicity until the end of the experiment. Ovulation rate was determined by counting the number of corpora lutea observed during laparoscopic examinations approximately 5 days after estrus during three estrous cyles following treatment. The ovulation rate between control and immunized groups was compared by repeated measures ANOVA. Immunization of the Malpura ewes against the synthetic peptide sequence of the α-subunit of bovine inhibin [bIα(1–29)Tyr30] increased ovulation rate over 5-fold compared to that of controls (Table 1). In conclusion, we have shown that inhibin-based fecundity vaccines have the potential of increasing ovulation rates in the Malpura breed of sheep.
|


