12 CASA PARAMETERS OF FRESH BULL SEMEN COLLECTED BY ARTIFICIAL VAGINA OR ELECTROEJACULATION IN ARGENTINA
G. Brogliatti A , F. Garcia Migliaro A , R. Cavia A , G. Larraburu A and A. Albrecht AReproduction, Fertility and Development 17(2) 156-156 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv17n2Ab12
Submitted: 1 August 2004 Accepted: 1 October 2004 Published: 1 January 2005
Abstract
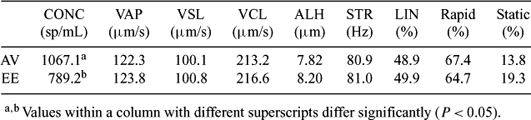
The latest entry in the field of semen evaluation is computer assisted semen analysis (CASA). Its greatest advantages are elimination of the subjective nature of routine semen evaluation and the addition of detailed motion analysis unquantifiable by visual examination. The objective of this study was to evaluate CASA motility parameters of fresh bull semen collected by artificial vagina (AV) or electroejaculation (EE) from a total of 56 beef different bulls. Semen samples from a total of 45 beef bulls were collected by AV from winter to the end of spring (740 collections), and from 11 beef bulls by EE (120 collections) in the same period. First and second AV collections were analyzed as individual data. EE collection was performed only one. Means and standard deviations for each characteristic were calculated, compared, and statistically analyzed. A sample of the collection was diluted 1:20 in a semi-defined semen extender (Andromed, Minitüb, Tiefenbach, Germany) and held in a glass tube at 36°C for 5 min before analysis. The sample was loaded into 20-μm chambers, and six microscope fields from each chamber were analyzed. The following sperm motility parameters were determined with the Ceros 12.1 sperm analyzer (Hamilton Thorne Biosciences, Inc., Beverly, MA, USA) on at least 1000 spermatozoa:concentration (CONC), velocity average path (VAP), velocity straight line (VSL), curvilinear velocity (VCL), amplitude lateral head (ALH), beat cross frequency (BCF), straightness (STR), linearity (LIN), and percentage of rapid or statics cells. There were no significant differences (P > 0.05) in VAP, VSL, VCL, ALH, STR, LIN, and the percentage of rapid and static cells of semen collected by AV or EE. The concentration (sperm/mL) of the AV-collected sperm was significantly higher than for the sperm collected by EE. Results from the analysis indicate that semen collected by artificial vagina have motility characteristics similar to those collected by electroejaculation. More research needs to be done to evaluate motility parameters of frozen/thawed semen collected by electroejaculation and by artificial vagina.
|
This research was supported by Centro Genético Bovino de EOLIA sa Argentina.


