A least-squares minimisation approach to depth determination from numerical second horizontal self-potential anomalies
El-Sayed Mohamed Abdelrahman 1 2 Khalid Soliman 1 Khalid Sayed Essa 1 Eid Ragab Abo-Ezz 1 Tarek Mohamed El-Araby 11 Geophysics Department, Faculty of Science, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt.
2 Corresponding author. Email: sayed5005@yahoo.com
Exploration Geophysics 40(2) 214-221 https://doi.org/10.1071/EG08123
Submitted: 14 March 2008 Published: 17 June 2009
Abstract
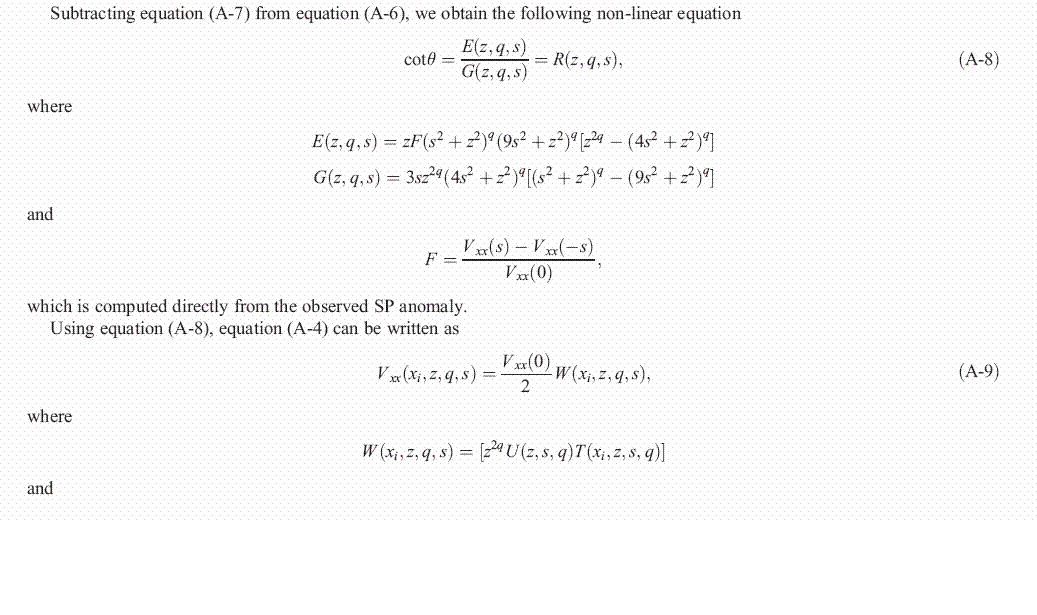
This paper develops a least-squares minimisation approach to determine the depth of a buried structure from numerical second horizontal derivative anomalies obtained from self-potential (SP) data using filters of successive window lengths. The method is based on using a relationship between the depth and a combination of observations at symmetric points with respect to the coordinate of the projection of the centre of the source in the plane of the measurement points with a free parameter (graticule spacing). The problem of depth determination from second derivative SP anomalies has been transformed into the problem of finding a solution to a non-linear equation of the form f(z) = 0. Formulas have been derived for horizontal cylinders, spheres, and vertical cylinders. Procedures are also formulated to determine the electric dipole moment and the polarization angle.
The proposed method was tested on synthetic noisy and real SP data. In the case of the synthetic data, the least-squares method determined the correct depths of the sources. In the case of practical data (SP anomalies over a sulfide ore deposit, Sariyer, Turkey and over a Malachite Mine, Jefferson County, Colorado, USA), the estimated depths of the buried structures are in good agreement with the results obtained from drilling and surface geology.
Key words: least-squares method, second derivative method, SP interpretation, simple models.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr L. Thomas, the Managing Editor, Dr S. Hall, the Associate Editor, Dr B. Bhattacharya, and a capable reviewer for their excellent suggestions and thorough review that improved our original manuscript.
Abdelrahman, E. M., and Sharafeldin, S. M., 1997, A least squares approach to depth determination from residual self-potential anomalies caused by horizontal cylinders and spheres: Geophysics 62, 44–48.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Corwin, R. F., and Hoover, D. B., 1979, The self-potential method in geothermal exploration: Geophysics 44, 226–245.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
El-Araby, H. M., 2004, A new method for complete quantitative interpretation of self-potential anomalies: Journal of Applied Geophysics 55, 211–224.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Patella, D., 1997, Introduction to ground surface self-potential tomography: Geophysical Prospecting 45, 653–681.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Yüngül, S., 1950, Interpretation of spontaneous polarization anomalies caused by spherical ore bodies: Geophysics 15, 237–246.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |


|
|

|
Error: Incorrect filename or format (EG08123_A1D.gif). Please check out

