First record of Ceratocystis fimbriata associated with shisham (Dalbergia sissoo) decline in Pakistan
Gul Bhar Poussio A , Munawar Raza Kazmi A , Chrys Akem B C and Faisal Sohail Fateh AA National IPM Program, Institute of Plant & Environmental Protection, National Agricultural Research Centre, Park Road, Shehzad Town, Islamabad, Pakistan.
B Queensland Primary Industries and Fisheries, DEEDI, Ayr Research Station, Ayr, Qld 4807, Australia.
C Corresponding author. Email: Chrys.Akem@dpi.qld.gov.au
Australasian Plant Disease Notes 5(1) 63-65 https://doi.org/10.1071/DN10023
Submitted: 8 June 2009 Accepted: 29 May 2010 Published: 21 June 2010
Abstract
Ceratocystis fimbriata has been associated with decline disorders of several fruit and forest trees. In 2006 this pathogen was isolated for the first time from declining mango trees in Pakistan. It has also recently been isolated from samples of declining shisham trees and pathogenicity tests have confirmed that it is indeed responsible for the decline disorders observed on shisham tress in Pakistan. This is the first record of C. fimbriata in association with shisham decline and the first time it is demonstrated to be the etiological agent of this important disease.
Shisham (Dalbergia sissoo), a member of the Fabaceae, is an important forest tree in Pakistan, the Indian sub-continent and other parts of the world. The tree was introduced into Pakistan a century ago from Nepal (Khan et al. 2004). It is attacked by a number of diseases among which decline, quick wilting or sudden death are the most important. This problem is not unique to Pakistan and has been reported from various countries where the shisham tree is grown (Bajwa et al. 2003). However, the severity of the decline disorder varies from country to country and regionally within the same country. In Bangladesh, for example, it has caused up to 55% mortality of the shisham population (Webb and Hossain 2005), while in Pakistan it has destroyed up to 80% of the tree populations along canal banks and up to 40% along highways and roadsides in the Punjab province (Bajwa et al. 2003).
The symptoms of the disease include initial dieback of branches and later, bark splitting and gummosis from the main stems which result finally in tree death (Fig. 1). Other symptoms also observed on infected trees are: wilting, cankers, internal chlorosis and necrosis (Fateh et al. 2006). Many fungi have been reported to be associated with shisham decline. These include: Fusarium solani (Bakshi 1954), Ganoderma lucidum (Sharma et al. 2000), Phytophthora cinnamomi (Gill et al. 2001) and Botryodiplodia theobromae (Khan et al. 2004).

|
Ceratocystis fimbriata (Ceratocystiaceae: Microascales) has been reported from a number of hosts around the world showing similar decline symptoms. These include mango (Mangifera indica), coffee (Coffea arbica), apricot (Prunus armeniaca), almond (Prunus amygdalus), Eucalyptus spp (Baker et al. 2003), citrus (Citrus sp.) (Borja et al. 1995) and rubber (Hevea brasilliensis) (Silveira et al. 1994). No previous record was found in the literature of an association of this fungus with shisham decline, but a possible association of this fungus with the disease was conjectured because of symptom similarities between shisham decline and mango decline caused by C. fimbriata.
In October 2008, samples were collected from the collar portions of declining shisham trees in the vicinity of the National Agriculture Research Centre (NARC), Islamabad, Pakistan, using a sharp axe. The wood samples were further cut into small pieces, placed in a plastic bag and taken to the NARC research laboratory. In the lab, the pieces were washed with distilled water, surface sterilised in 10% commercial bleach for 1 min and then dried over sterilised filter paper for 1 h. Some of the pieces were then aseptically transferred to the centre of 90-mL Petri plates containing potato dextrose agar (PDA) and incubated at 20 ± 2oC.
Ten days after incubation, the growing colonies from the wooden pieces were sub-cultured to fresh PDA plates and incubated under the same conditions for further growth and sporulation. Ten days later, the fungal colonies were examined under a compound microscope (Labomed LX-400 fluorescent microscope; Hicksville, NY, USA). Fungal structures were mounted on 70% ethanol followed by an additional drop of lactophenol for observation under the microscope.
The sporulating fungi obtained from the stem pieces had a morphology equivalent to that of C. fimbriata, as described in Morgan-Jones (1967), and Fusarium solani which has recently been described and reported to be associated with shisham decline (Rajput et al. 2010). However, C. fimbriata is recorded here for the first time in association with shisham decline. The fungus obtained from diseased trees had the following morphology: mycelium initially hyaline becoming mouse-grey or greenish brown. After 5 days the conidiophores gave rise to large numbers of conidia in chains with hyaline and dark pigmented colours; perithecia globose (140–200 µm), black with a long neck, 700–800 µm long; ascospores hat-shaped, 4–8 µm × 2–5 µm, hyaline (Fig. 2); conidia of two kinds: catenulate, rectangular, truncated, 11–18 µm × 4–6 µm, hyaline endoconidia and cantenulate, oval, 8–16 × 5–12 µm, thick-walled, brown, aleuriconidia (Fig. 3). The cultures of C. fimbriata were deposited in the collection of the Department of Mycology and Plant Pathology, Quaid-i-Azam campus, University of Punjab, Lahore-Pakistan (accession number FCBP 1012).
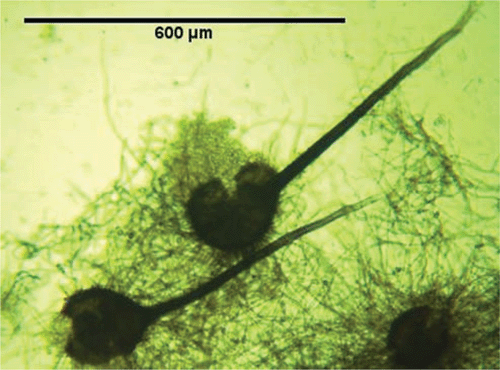
|
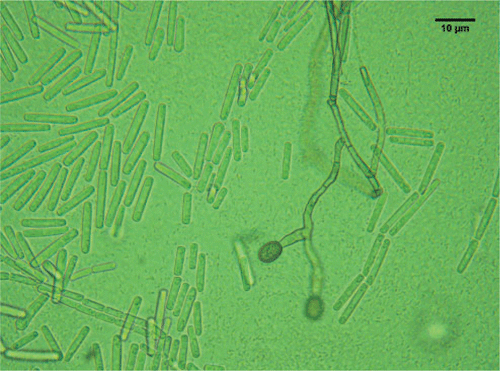
|
A pathogenicity test was carried out in order to confirm the association of the isolated fungi with the disease. A total of 20 18-month-old shisham plants, each 115–120 cm tall, grown in pots in greenhouse conditions, were used. The inoculations were carried out with C. fimbriata and F. solani isolates from the declining trees separately and also in combination with the two fungi. Five plants were inoculated in each treatment, using a flap method normally used for such stem inoculations. A T-shaped incision (1.5 cm long) was made in the collar portion of the stem up to a depth of 4–5 mm and a 5 mm mycelial plug taken from freshly grown cultures of each fungus was placed below the bark at the incision site and the area was sealed with Parafilm (Iqbal et al. 2010). Five plants with a similar flap injury were inserted with only culture medium plugs and served as controls. Observations were then made on every other day for any symptom developments.
Decline symptoms were observed after 8 weeks, both on plants inoculated with C. fimbriata individually and on plants inoculated with C. fimbriata combined with F. solani. (Fig. 4). Plants inoculated with C. fimbriata alone, showed drooping of leaves, bark splitting 2–3 inches above inoculation point oozing gum. When the bark was removed at these sites, necrotic dark brown to black tissue was observed. Similar symptoms were observed in the case of combination treatments with C. fimbriata and F. solani. No conspicuous symptoms were observed on the five plants inoculated with F. solani alone, although a few leaves dried up on some of the plants. Control plants remained healthy. Both fungi were reisolated from the diseased plants, thus confirming the association of C. fimbriata alone and in combination with F. solani with the shisham tree decline disease. Further molecular studies are in progress to determine whether C. fimbriata from shisham is the same fungus involved in mango decline. Ceratocystis fimbriata is known to be a large complex of species and a more precise identification of the population attacking shisham is of significance for better understanding of this important disease and its management.

|
Baker CJ,
Harrington TC,
Kraus U, Alfenas AC
(2003) Genetic variability and host specialization in the Latin American clad of Ceratocystis fimbriata. Phytopathology 93, 1274–1284.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
CAS |
PubMed |

Bakshi BK
(1954) Wilt of shisham (Dalbergia sissoo Roxb.) due to Fusarium solani, the wilt organism in the soil. Nature 174, 278–279.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

Bajwa R,
Javid A, Shah MBM
(2003) Extent of Shisham (Dalbergia sissoo Roxb.) decline in Sialkot, Gujranwala, Lahore and Sargodha Districts. Mycopathology 1, 1–5.

Fateh FS,
Kazmi MR,
Ahmad I, Ashraf M
(2006) Ceratocystis fimbriata isolated from vascular bundles of declining mango trees in Sindh, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Botany 38, 1257–1259.

Iqbal Z,
Pervez MA,
Saleem BA,
Ahmad S,
Dasti AA, Saleem A
(2010) Potential of Fusarium mangiferae as an etiological agent of mango malformation. Pakistan Journal of Botany 42, 409–415.

Khan SH,
Idrees M,
Muhammad F,
Mahmood A, Zaidi SH
(2004) Incidence of Shisham (Dalbergia sissoo Roxb.) decline and in vitro response of isolated fungus sp. to various fungicides. International Journal of Agricultural Biology 6, 611–614.
|
CAS |

Rajput NA,
Pathan MA,
Rajpoot AQ,
Jiskani MM,
Lodhi AM,
Rajput SA, Khaskheli MI
(2010) Isolation of fungi associated with shisham trees and their effect on seed germination and seedling mortality. Pakistan Journal of Botany 42, 369–374.

Silveira AP,
Oliveira DA,
Cardoso RMG,
Neto FB,
Ortolani AA, Godoy G
(1994) Caracterização do prejuízo provocado pelo mofo cinzento (Ceratocystis fimbriata) em painéis de seringueira (Hevea brasiliensis). Summa Phytopathologica 20, 196–199.

Webb EL, Hossain SMY
(2005) Dalbergia sissoo mortality in Bangladesh plantations: correlations with environmental and management parameters. Forest Ecology and Management 206, 61–69.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |



