Australian Journal of Zoology
Volume 67
Number 4 2019
The avifauna of urban Longueville changed dramatically between 1971 and 2014. Of the 31 most common native birds, 17 declined and were absent in 2014, while 14 increased, including 7 species absent or very rare in 1971. Two increasers, the noisy miner and the rainbow lorikeet, are now dominant. Overabundance of the highly aggressive noisy miner, which we suggest is linked to increased planting of nectar-rich Australian plants in gardens, appears to be the chief cause of the decline of small native birds at Longueville.
Photo by Peter Smith.
Juveniles of the bumphead parrotfish, Bolbometopon muricatum, the largest fish herbivore and coral predator associated with coral reefs, are extremely scarce on the Great Barrier Reef. We report the southernmost observation of this species on the Great Barrier Reef and southernmost observation of a juvenile anywhere, from off Heron Island in the Capricorn–Bunker region.
Photo by Kristen T. Brown.
The snouts of living lungfish are exposed to hazards in the environment, as they gather food among rocks on the bottom of the river. They have a thick epithelium on the snout, penetrated by lymphatic vessels arising from the blood vessels below the epithelium to protect the fish from infection. Fossil lungfish from Devonian deposits that fed in a similar way also have lymphatic vessels that enter the outer layers of the skin.
Photo by Anne Kemp.
It is important to identify the resources that cause increases in primary prey items of the threatened eastern grass owl (Tyto longimembris). I conducted area searches across spring and summer in wetlands of Kooragang Island, NSW, to determine abundance of prey items in relation to prey food sources. I found increased house mice abundance during the flowering period of a wetland plant, and observed grass owls during only one of these periods.
Photo by Matt Wright.
How many feral pigs occur in Australia? Mean abundance differed between 4.4 million, 3.0 million and 3.2 million in the 1980s, 1990s and 2000s respectively. Abundance estimates are lower and more precise than a previous estimate (13.5 million), so scientists and managers should revise their use of estimates.
Photo by Peter West.
In this study, Google Trends data were used to examine the seasonality of the search term ‘thylacine sightings’ and the development of the frequency of other search terms in the period between 2004 and 2020. While Google Trends cannot clearly determine search motivation, terms that document the hope of a possible survival of thylacine, for example, can come to the fore, as can a more rational or concern-triggered interest in the Devil Facial Tumour Disease, for example.
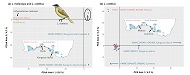
Using single nucleotide polymorphisms and mitochondrial DNA sequences we find some evidence of genetic structure within a widespread and naturally fragmented species, the purple-gaped honeyeater (Lichenostomus cratitius), of southern Australian mallee shrublands. The very earliest stages of differentiation either side of the Nullarbor Barrier may already have been arrested by gene flow, some of which may have been anthropogenically induced.
Globally, montane amphibian species are under severe pressure from climate change. Despite this, basic monitoring is lacking for many of these species. In this study, we found that the mountain frog (Philoria kundagungan) has a highly restricted and fragmented distribution, being limited to ~11 km2 of potentially suitable habitat. In light of the continued pressures of climate change, the results of our surveys and the approach used will be vital for assessing the impacts and formulating management actions.
Photo by Liam Bolitho.