Soil chemistry and morphology transects to assist wetland delineation in four semi-arid saline lakes, south-western Queensland
A. J. W. Biggs A C , K. Bryant B and K. M. Watling AA Department of Environment and Resource Management, Toowoomba, Qld 4350, Australia.
B Department of Environment and Resource Management, Indooroopilly, Qld 4067, Australia.
C Corresponding author. Email: andrew.biggs@derm.qld.gov.au
Australian Journal of Soil Research 48(3) 208-220 https://doi.org/10.1071/SR09127
Submitted: 15 July 2009 Accepted: 5 November 2009 Published: 6 May 2010
Abstract
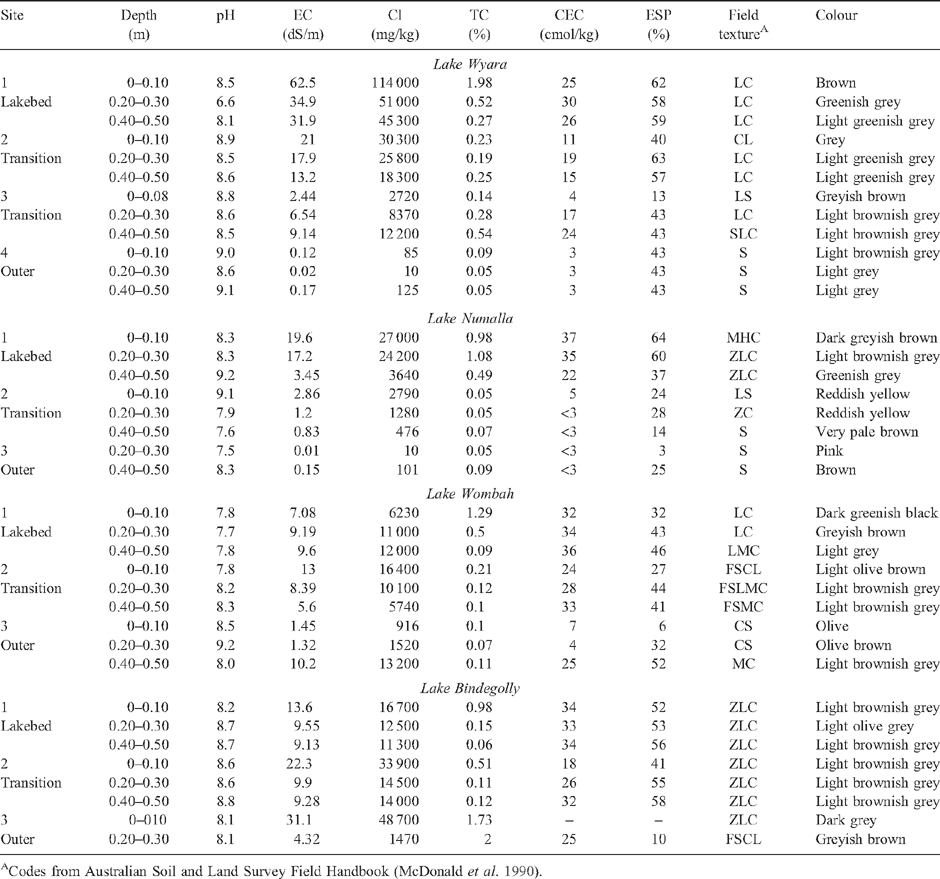
Soils at 4 saline lakes (Wyara, Numalla, Wombah and Bindegolly) in semi-arid south-western Queensland were described and sampled to determine soil attributes that assist in the delineation of wetlands. Up to 4 sites were described in transects perpendicular to the lake edge. Samples from fixed depths were analysed for limited ionic chemistry and, in some cases, selected acid sulfate soil parameters. Lakebed soils were alkaline Hypersalic Hydrosols, changing to a variety of soils, including alkaline Rudosols and Podosols on adjacent lunettes and beach ridges. Gley colours and mottling were indicative of lakebed soils, while redder colours and stratification were common in soils outside the wetland. Evaporative concentration of salts at the soil surface was common in lakebed and transition zone soils, whereas leaching of salts was common in sandier soils outside the wetlands. Analysis of acid sulfate soil parameters and field evidence in the beds of Lakes Wyara and Wombah confirmed the presence of unoxidised sulfidic sediments and extensive neutralising capacity. Wave action formation of beach ridges appeared to be the most prevalent land-forming process at 3 lakes, but wind-driven deflation with associated lunette-building was evident at Lake Bindegolly. The data confirmed the value of pedological features such as texture, colour, and salinity trends in determining the boundaries of these wetlands, but also highlighted the transient nature of these features.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to recognise the assistance of Peter Wilson, Dan Brough, Lauren Eyre, Neil Cupples, and staff of the Queensland Environmental Protection Agency for assistance in fieldwork; Shawn Darr for cartography, and staff of the NRSc analytical centre. The editorial comments of Col Ahern and 2 anonymous reviewers are acknowledged.
Briere PR
(2000) Playa, playa lake, sabkha: Proposed definitions for old terms. Journal of Arid Environments 45, 1–7.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

De Deckker P
(1988) Biological and sedimentary facies of Australian salt lakes. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 62, 237–270.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
CAS |

Hall KC,
Baldwin DS,
Rees GN, Richardson AJ
(2006) Distribution of inland wetlands with sulfidic sediments in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. The Science of the Total Environment 370, 235–244.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
CAS |
PubMed |

Knight MJ,
Saunders BJ,
Williams RM, Hiller J
(1989) Geologically induced salinity at Yelarbon, Border Rivers area, New South Wales, Queensland. Journal of Australian Geology and Geophysics 11, 355–361.
|
CAS |

Timms BV
(1993) Saline lakes of the Paroo, inland New South Wales, Australia. Hydrobiologia 267(1–3), 269–289.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
CAS |

Timms BV
(1998) A study of Lake Wyara, an episodically filled saline lake in southwest Queensland, Australia. International Journal of Salt Lake Research 7, 113–132.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

Timms BV
(2001) A study of the Werewilka Inlet of the saline Lake Wyara, Australia a harbour of biodiversity for a sea of simplicity. Hydrobiologia 466, 245–254.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

Timms BV
(2006) The geomorphology and hydrology of saline lakes of the middle Paroo, arid-zone Australia. Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales 127, 157–174.

Timms BV
(2008) The ecology of episodic saline lakes of inland eastern Australia, as exemplified by a ten year study of the Rockwell-Wombah Lakes of the Paroo. Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales 129, 1–16.

Timms BV, Boulton AJ
(2001) Typology of arid-zone floodplain wetlands of the Paroo River (inland Australia) and the influence of water regime, turbidity, and salinity on their aquatic invertebrate assemblages. Archiv fuer Hydrobiologie 153(1), 1–27.

|


