Reproduction, Fertility and Development
Volume 36
Number 18 2024
This review summarises the major findings from the 2023 Society for Reproductive Biology conference. We discuss topics of environmental impacts on reproduction, reproductive cancers, cellular basis of reproduction, evolution of reproductive mechanisms, and inclusivity in reproductive health. Image generated in Adobe Illustrator using AI.
This article belongs to the collection: Frontiers in Reproduction Science – Rising Stars at the Society for Reproductive Biology 2023.
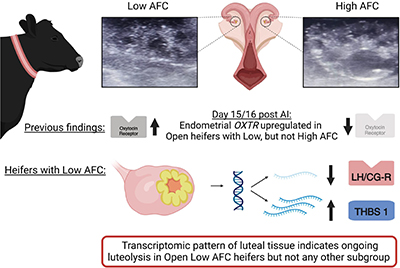
Livestock production systems rely on efficient reproduction. Selection of heifers with a high number of antral ovarian follicles can be applied with the aim of improving reproductive efficiency. The herein presented results support an earlier onset of luteolysis in non-pregnant heifers with a low number of antral follicles. This indicates a shorter time period for the recognition of pregnancy by the dam, which might contribute to inferior reproductive performance in heifers with a low number of antral ovarian follicles. Image by MK, created with biorender.com.
This article belongs to the collection: The biology of the ovary – Honouring the contributions of Ken P McNatty and Rex J Scaramuzzi.
Melatonin is a hormone that has effects on various organs and is produced mainly by the epiphysis. The administration of melatonin influences the vitality and weight of the lamb at birth, and the production and quality of the mother’s milk. The use of this hormone during pregnancy can mitigate the effect of birth stress on the lamb and the mother. Photograph by Vincenzo Carcangiu.
This article belongs to the collection: Non-photoperiodic Actions of Melatonin.
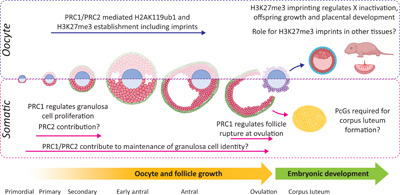
Epigenetic information is an additional layer of information on top of our genes that influences which genes are active in a given cell type. This information is critically important, but we do not fully understand how it is regulated in the ovary or eggs that give rise to the next generation. This review summarises recent discoveries exploring how epigenetic information is regulated in the ovary. Diagram by Ellen G. Jarred.
This article belongs to the collection: Frontiers in Reproduction Science – Rising Stars at the Society for Reproductive Biology 2023.