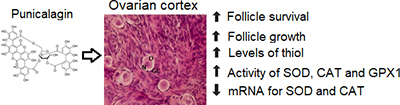
The in vitro overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) impairs follicular growth and survival. This study evaluated the effects of punicalagin on growth and survival of primordial follicles, stromal cells, collagen fibres, levels of mRNA and activity of antioxidant enzymes in cultured bovine ovarian tissues. The results showed that punicalagin improved follicle survival and development, and reduced mRNA levels for SOD1 and CAT. Punicalagin 10.0 μM increased the levels of thiol and activity of SOD1, CAT and GPX1 enzymes. Image by V. S. Bezerra.

Reproduction, Fertility and Development
Volume 36 Number 13 2024
Preeclampsia is one of the common complications of pregnancy, posing a significant risk to the life and health of the pregnant woman and fetus, which is why it is so important to achieve predictability and determine the risks of the disease. This research aims to determine the pathogenetic role of several factors in the development of preeclampsia and its progression in association with the severity of pregnant patients. Sixty pregnant women diagnosed with preeclampsia, both mild and severe, were enrolled. Forty healthy pregnant women were also studied for comparison. Image by Irina Ismailova.
Understanding complex biological data is crucial for advancements in reproductive biology. Our study developed ShinySperm, a web application that allows researchers to easily explore, interrogate, and visualise intricate sperm proteomic data. This tool sets out a blueprint for future research, enabling researchers to bring their intricate datasets to life, allowing others to interact with and interpret more effectively, ultimately driving innovation in reproductive biology. Image by David Skerrett-Byrne.
This article belongs to the Collection Frontiers in Reproduction Science – Rising Stars at the Society for Reproductive Biology 2023.
RD24079 Abstract | RD24079 Full Text | RD24079PDF (1.1 MB) | RD24079Supplementary Material (746 KB) Open Access Article
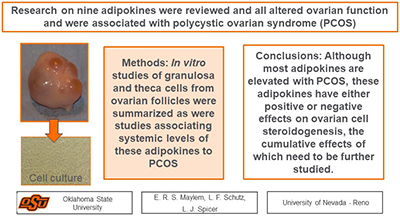
Adipose tissues produce a variety of biologically active compounds including adipokines, which function as endocrine hormones that are linked to various metabolic and reproductive diseases. The goal of this review was to provide an up-to-date summary of the role of some of these adipokines in mammalian reproduction and how they regulate ovarian steroid production. Understanding the effects of these adipokines on ovarian function will help formulate solutions for improved reproductive efficiency. Image by Leon Spicer.