81 EFFECT OF SUCROSE CONCENTRATION IN WARMING MEDIUM ON THE DEVELOPMENT POTENTIAL OF VITRIFIED BOVINE OOCYTES
W.C. Chang A , J. Xu B , S. Jiang A , X.C. Tian A , X. Yang A and F.L. Du AA Department of Animal Science, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT 06269, USA
B Evergen Biotechnologies, Inc., Storrs, CT 06269, USA. Email: jxu@evergen.com
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 17(2) 190-191 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv17n2Ab81
Submitted: 1 August 2004 Accepted: 1 October 2004 Published: 1 January 2005
Abstract
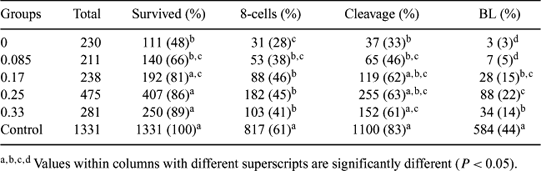
The aim of this experiment was to determine the effect of the sucrose concentration (0 to 0.33 M) in the dilution medium on the viability, fertilizability, and development of vitrified bovine oocytes. Bovine oocyte-cumulus complexes were collected from slaughterhouse ovaries and in vitro-matured as reported previously. After 24-h maturation in TCM199-based medium under 5% CO2 humidified air at 39°C, these were exposed to hyaluronidase and carefully pipetted to remove all except the 3–5 innermost layers of cumulus. Oocytes were put into the pre-equilibration medium for 3 min and then into vitrification solution containing HEPES-buffered TCM199 supplemented with 20% FBS, ethylene glycol, and dimethylsulphoxide for 25–30 s; they were then vitrified by modified solid surface vitrification (Dinnyes et al. 2000 Biol. Reprod. 63, 513–518).The oocytes were warmed at 39°C by placing them in holding medium with 0, 0.08, 0.17, 0.25, or 0.33 M sucrose. Non-vitrified oocytes were used as controls. Oocytes were inseminated 30 min after warming, and the presumptive zygotes were cultured in CR1-aa medium supplemented with 6 mg/mL BSA at 39°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2, 5% O2, and 90% N2 for eight days. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. As shown in Table 1, there was no significant difference in survival rate (P > 0.05) of the vitrified oocytes that were placed in dilution solution containing 0.17, 0.25, or 0.33 M sucrose and the non-treated controls. On Day 2 (fertilized on Day 0), cleavage to the 8-cell stage was similar for the 0.17, 0.25, and 0.33 M dilution groups, but the rates for all three were significantly lower (P < 0.05) than for the control group. The blastocyst rate on Day 8 was significantly higher for the 0.25 M group than for any other experimental group but still significantly lower than for the control. In conclusion, this study suggests that with this vitrification/warming procedure the optimum concentration of sucrose in the dilution solution is 0.25 M.
|
The authors would like to thank Ms Colleen Shaffer for the preparation of bovine oocytes.


