Natural occurrence of Cucumber mosaic virus on lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus), a new record
S. K. Raj A C , S. Kumar A , D. Pratap A , R. Vishnoi A , S. Choudhari A and S. Chandra BA Molecular Virology Laboratory, National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow 226 001, India.
B Biodiversity and Applied Botany Division, Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine, Jammu-Tawi 180 001, India.
C Corresponding author. Email: skraj2@rediffmail.com
Australasian Plant Disease Notes 2(1) 95-96 https://doi.org/10.1071/DN07039
Submitted: 10 May 2007 Accepted: 12 June 2007 Published: 22 June 2007
Abstract
The natural occurrence of Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) on Cymbopogon citratus was detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay using antiserum raised against CMV and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction using specific primers for the coat protein. Sequence analysis of the PCR product showed 93–97% identities and a close phylogenetic relationship with CMV isolates of subgroup Ib.
Lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus, family Poaceae) is a perennial herb, commercially cultivated in an ~3000 ha area in Kerala, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh and Assam states of India, with an annual production of 300–350 t (http://hortibizindia.org/Horticulture%20Crops%5CLemongrass%5CLemongrass1.htm). The essential oil obtained from this herb has been reported to have antimicrobial activity, and is being used in medicines (as a central nervous system depressant), cosmetics and confectionary (Simon et al. 1984). Severe yellow stripes and tip necrosis of leaves were observed on C. citratus growing naturally at Chattha Research Farm of IIIM, Jammu-Tawi, India in 2005–06. The causal pathogen was transmitted by mechanical inoculations using sap of infected leaves, which resulted in local necrotic lesions on Chenopodium amaranticolor and systemic mosaic on Nicotiana tabacum cv. White Burley. The virus reacted positively with the antiserum raised against Cucumber mosaic virus (PVAS 242a, American Type Culture Collection, USA) in enzyme linked immunosorbent assay tests indicating the association of CMV with the leaf stripe disease of lemongrass.
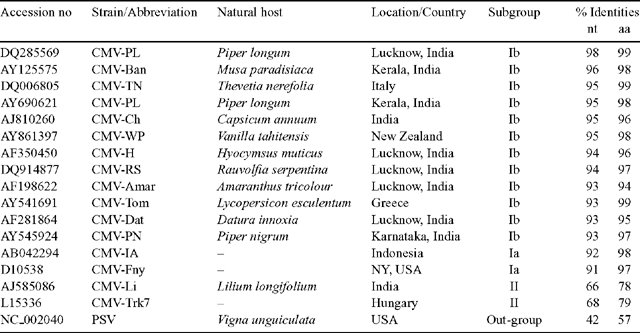
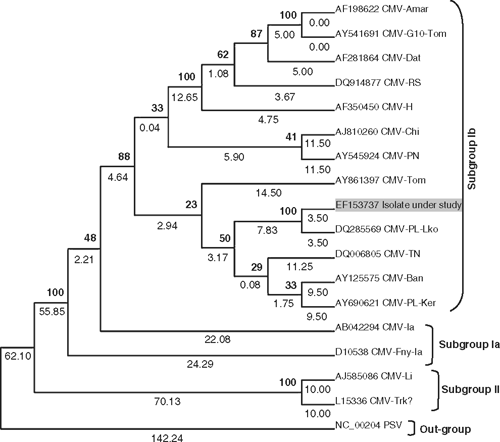
To identify the virus isolate at the molecular level, total RNA was isolated by the method of Spears and Longhurst (1993) from infected and apparently healthy leaf tissues of C. citratus and the reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed using the primers for the coat protein gene region of CMV (AM108922/AM108923; Srivastava et al. 2004). Electrophoresis of the RT-PCR products resulted in an amplicon of the expected size (~650 bp) in the infected but not in the healthy samples. The RT-PCR amplicon was cloned and sequenced (GenBank Accession number EF153737). Sequence analysis extended over the complete coat protein open reading frame of 657 nucleotides, encoding 218 amino acid residues. Genomatix DiAlign analysis of accession EF153737 with twelve other CMV isolates reported from India and elsewhere in the world revealed 93–98% identities at the nucleotide and 95–99% at the amino acid level (Table 1). The lemongrass virus isolate showed closest phylogenetic relationships with CMV isolates belonging to subgroup Ib (Fig. 1).
|
|
There is no published record of any virus disease on C. citratus available except the rust and leaf spot diseases caused by Puccinia nakanishikii in California (Koike and Molinar 1999) and Curvularia verruciformis in India (Barua and Bodoloi 1983). To our knowledge this is the first record of the natural occurrence of CMV on C. citratus.
Acknowledgements
The authors express gratitude to the Directors NBRI, Lucknow and IIIM, Jammu-Tawi for permission and CSIR, New Delhi for the fellowships to S. Kumar and D. Pratap.
Barua A, Bodoloi DN
(1983) Record of a new disease of Lemongrass (Cymbopogon flexuosus Stapf) caused by Curvularia verruciformis Agrawal and Sahni. Current Science 52, 13–14.

Koike ST, Molinar RH
(1999) Rust Disease on Lemongrass in California. Plant Disease 83, 304.
| Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |

Srivastava A,
Chandra G, Raj SK
(2004) Molecular characterization of a strain of Cucumber mosaic virus based on coat protein and movement protein genes. Acta Virologica. English Ed. 48, 229–239.



