
Australian Journal of Chemistry
Volume 71 Number 8 2018
CH18192Visible Light-Induced CO-Release Reactivity of a Series of ZnII–Flavonolate Complexes
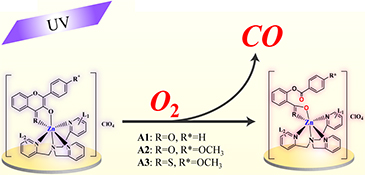
A series of zinc–flavonolate complexes have been prepared and characterised. Exposure of the complexes to visible light in aerobic conditions results in oxidative C–C bond cleavage and CO release. The order of the maximum absorption wavelength of the complexes showed A3 > A2 > A1.
CH18138Efficient Hydrolytic Breakage of β-1,4-Glycosidic Bond Catalyzed by a Difunctional Magnetic Nanocatalyst
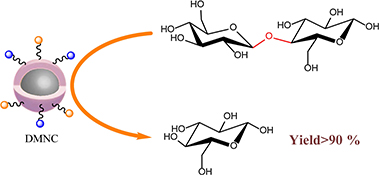
A magnetic nanocatalyst, which could be used to catalyse the hydrolytic breakage of β-1,4-glycosidic bonds, was prepared. This recyclable nanocatalyst could efficiently catalyse the hydrolysis of cellobiose to glucose and cellulose to reducing sugar under relatively moderate conditions, and the catalytic system showed good selectivity of product.
CH18246An Efficient Synthesis of Pyrrolidinone Derivatives in the Presence of 1,1′-Butylenebis(3-sulfo-3H-imidazol-1-ium) Chloride
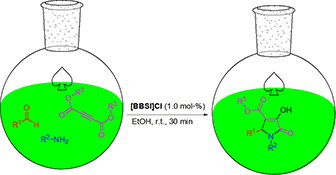
The application of 1,1′-butylenebis(3-sulfo-3H-imidazol-1-ium) chloride in the synthesis of 2-pyrrolidinones is described under mild conditions and the structure–activity relationship (SAR) is also investigated for this ionic liquid and some of the mono- and di-cationic ionic liquids containing the same counter-anion under optimized conditions.
CH18267Synthesis of a Highly Functionalised and Homochiral 2-Iodocyclohexenone Related to the C-Ring of the Polycyclic, Indole Alkaloids Aspidophytine and Haplophytine
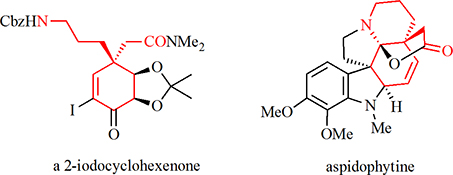
The synthesis of a homochiral 2-iodocyclohexenone related to the C-ring of the title alkaloids is reported.
CH18225The Utility of Calculated Proton Affinities in Drug Design: A DFT Study

Proton affinities can be accurately derived using DFT. Correlations between proton affinities and their pKas is good within chemical families. Categorisation based on functional groups results in reasonable linear relationships and predicting pKa of 90 drugs based on their proton affinities was moderately successful.
CH18148Evolution Analysis of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesised by Lactam Reduction: A Case Study of ϵ-Caprolactam

ϵ-caprolactam (CL) was used as a model to illustrate the evolution of silver nanoparticles in the lactam’s medium. This evolution includes two different stages: (1) particles being stabilised at <5 nm because of face-bound CL and (2) the Ostwald ripening cooperated with continuous Ag+ reduction, producing the resultant particles with different size distribution.
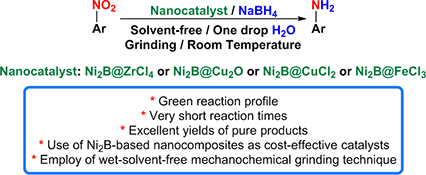
We report a simple synthesis of four new Ni2B-based nanocomposites, namely Ni2B@ZrCl4, Ni2B@Cu2O, Ni2B@CuCl2, and Ni2B@FeCl3, which were characterized by FT-IR, XRD, SEM, and EDX. The catalytic applications of these nanocomposites were successfully evaluated in the wet-solvent-free reduction of nitroarenes to arylamines with NaBH4 at room temperature by a mechanochemical grinding technique.
CH18252N,N-Dialkyl-N′-Chlorosulfonyl Chloroformamidines in Heterocyclic Synthesis. Part XV. Some Unexpected Reactions with Anilines

N,N-dimethyl-N′-chlorosulfonyl chloroformamidine 1a underwent reactions with various anilines 6 to give the benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine dioxides 8 and bis-anilino adducts 9, along with some unexpected products, particularly when sterically hindered anilines were used. In such cases, the [1,3,2,4,6]dithiatriazine 1,1,3,3-tetraoxides 17 and, on occasion, the 4-(arylimino)-[1,3,5]triazin-2-amines 14, were produced.




