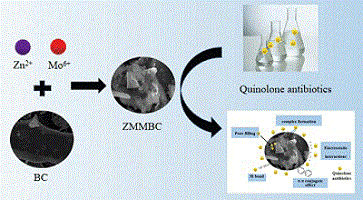
MoS2 and ZnS modified biochar (ZMMBC) was synthesised by hydrothermal method. The removal potential of pefloxacin (PF), levofloxacin (LF) and norfloxacin (NF) was studied. It only takes 90 min for ZMMBC to reach its maximum adsorption capacity. The adsorption behaviour mainly includes complexation, pore filling, π–π interactions, electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding interactions. (Image credit: Y.-J. Gan.)

Australian Journal of Chemistry
Volume 77 Number 4 2024
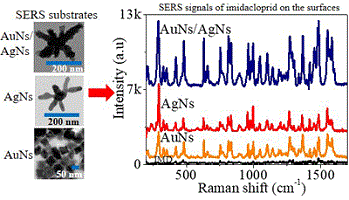
This manuscript reports the first introduction of gold nanostars on silver nanostars surface as the Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) active elements to increase the SERS response towards imidacloprid pesticide. This combination of two metal nanostars showed an enhancement in imidacloprid signal at low concentrations on the AuNs/AgNs surface when compared to the signal on the surface composed of a single type of metal nanostars. The substrates were shown to be stable over a month in storage and can be reused many times. (Image credit: N. Abu Bakar.)
CH23189 Abstract | CH23189 Full Text | CH23189PDF (3.4 MB) | CH23189Supplementary Material (804 KB) Open Access Article